Social media has become a pivotal driver in how companies find, attract, and hire talent. Platforms once used for social updates now serve as dynamic recruiting hubs, influencing every stage of talent acquisition, from sourcing passive candidates to employer branding. In the U.S. job market, employers increasingly blend LinkedIn outreach with Facebook job posts, while job seekers use social feeds to research companies and spot opportunities. Real-world applications include corporate talent teams using Instagram for employer branding and small businesses sourcing passive professionals via LinkedIn searches. Below, explore the latest recruitment statistics shaping hiring strategies.
Editor’s Choice
- 92% of recruiters worldwide use social media to source and engage candidates in 2026.
- 86% of job seekers actively use social platforms during their job search.
- 84% of companies leverage social media as part of their formal hiring strategy.
- 94% of recruiters use LinkedIn, Facebook, or Twitter for talent discovery.
- 82% of employers engage passive candidates via social media.
- 65% of organizations maintain dedicated social recruitment channels.
- 79% of job seekers want to see job opportunities posted on platforms like Facebook.
Recent Developments
- AI adoption in recruiting continues rising, with 66% of recruiters planning increased use of AI for pre-screening.
- Social recruiting is surpassing traditional job boards as a primary talent channel.
- Expanded use of hashtags, groups, and algorithmic talent matching enables more targeted candidate outreach.
- Social platforms now integrate live hiring events, stories, and reels to boost engagement efficiency.
- Employer branding campaigns on social show ~31% higher reach during optimized campaigns, such as summer schedules.
- Mobile social access drives more candidate traffic and faster responses to job posts.
- Increased emphasis on privacy and legal compliance when viewing candidate profiles.
- Real-time analytics dashboards on platforms like LinkedIn guide recruitment decisions.
Adoption of Social Media in Recruitment
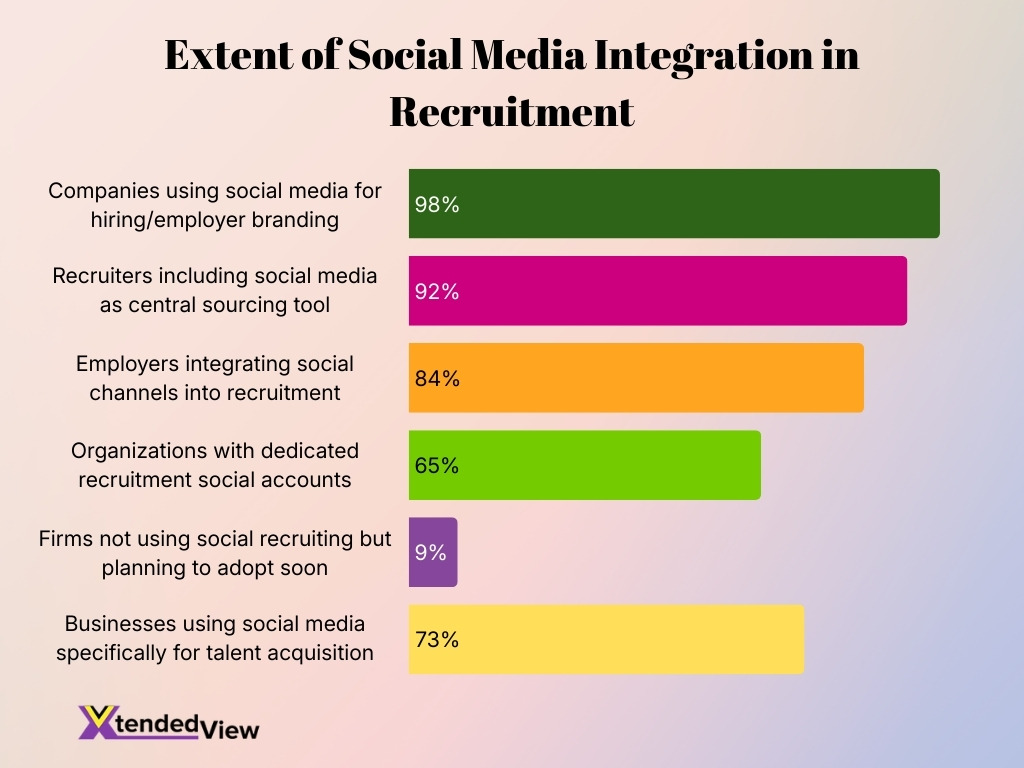
- 98% of companies use social media for hiring and employer branding.
- 92% of recruiters include social media as a central sourcing tool.
- 84% of employers have integrated social channels into their recruitment process.
- 65% of organizations operate dedicated recruitment social accounts.
- Only 9% of firms that are not currently using social recruiting plan to adopt it soon.
- 73% of businesses use social media specifically for talent acquisition functions.
- Social recruitment now plays a significant role in employer branding and candidate research.
- Companies with strong social recruitment see enhanced candidate pipeline depth and engagement.
Employer Usage Statistics
- 91% of employers use social media to recruit talent in 2026.
- 45% of recruiters post content to engage candidates on social platforms.
- 82% of employers use social recruiting to find passive job seekers.
- 60% of hiring managers use Facebook to search for talent.
- 73% of job seekers research a company’s social presence before applying.
- Employee advocacy is encouraged by 90% of recruiters to amplify social hiring content.
- Over 50% of employers screen candidates on social profiles.
- LinkedIn leads as the platform of choice for employer talent outreach.
Recruiter Usage Statistics
- 95% of recruiters use LinkedIn regularly as their primary hiring platform.
- 94% of recruiters use at least one major social channel (LinkedIn/Facebook/Twitter).
- 64% of recruiters use two or more social platforms for sourcing.
- 45% of recruiters post original content on social to attract candidates.
- Recruiters often screen candidate culture fit through social profiles.
- AI tools are increasingly blended into recruiters’ workflows.
- Recruiters cite social media as essential for employer branding strategies.
- LinkedIn recruiter tools are heavily used in talent pipelines.
Platform Usage by Recruiters: Key Adoption Trends
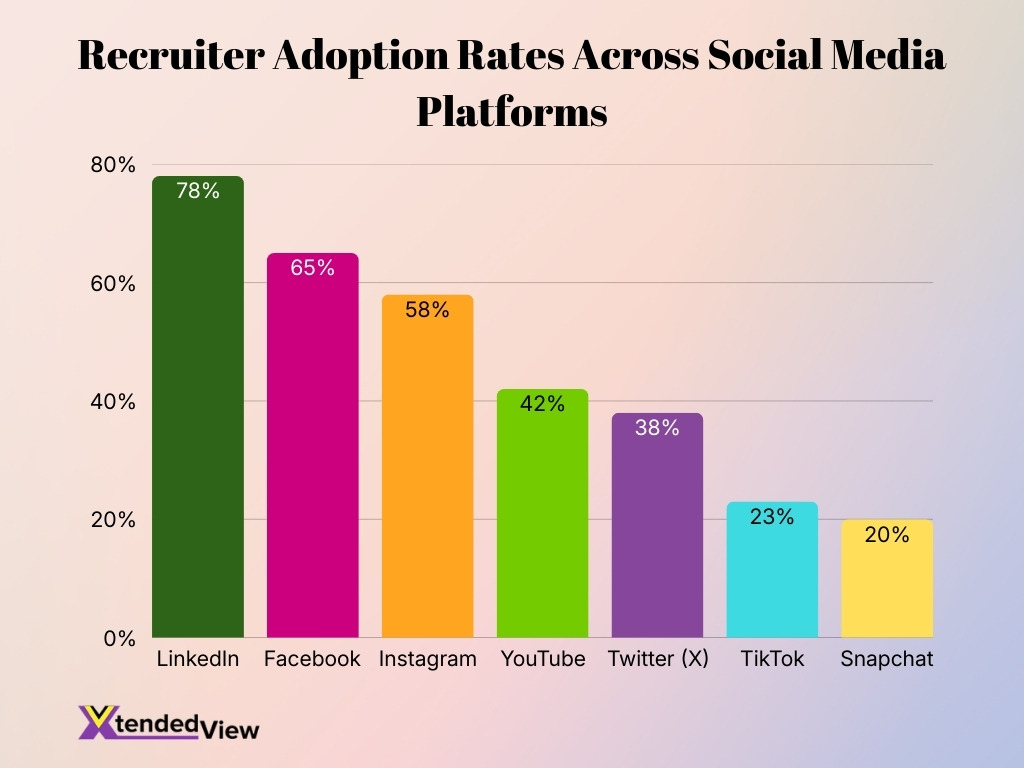
- LinkedIn dominates recruiter activity, with a leading adoption rate of 78%, making it the most trusted platform for professional hiring.
- Facebook remains a major recruitment channel, used by 65% of recruiters for job postings and employer branding.
- Instagram continues to grow in hiring relevance, with 58% adoption, driven by visual storytelling and Gen Z engagement.
- YouTube supports employer branding efforts, with 42% of recruiters leveraging video content to showcase workplace culture.
- Twitter (X) plays a secondary role in recruitment, with 38% usage, mainly for networking and real-time job updates.
- TikTok adoption is still limited, with only 23% of recruiters using it for talent acquisition and outreach.
- Snapchat ranks lowest in recruiter usage, at just 20%, reflecting minimal focus on professional recruitment.
- Professional-first platforms outperform entertainment apps, as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram together account for over 200% combined adoption.
- Visual and video-based platforms show rising influence, with YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok reaching a combined 123% usage among recruiters.
- Overall, recruiters prioritize credibility and reach, favoring platforms with established professional and business-oriented audiences.
LinkedIn Recruitment Statistics
- 95% of recruiters use LinkedIn as their primary sourcing tool.
- Over 67 million companies maintain active LinkedIn pages, supporting employer branding and recruitment marketing.
- 40% of LinkedIn users log in daily, increasing recruiter visibility and response rates.
- LinkedIn reports that 8 people are hired every minute through the platform.
- 72% of recruiters use LinkedIn to find passive candidates who are not actively applying.
- InMail response rates average 10–25%, significantly higher than traditional cold email outreach.
- Job posts with company videos on LinkedIn receive 36% more applications than text-only posts.
- LinkedIn Recruiter users report up to 20% faster time-to-hire when leveraging advanced search filters.
- Over 75% of job seekers research company LinkedIn pages before submitting applications.
Facebook Recruitment Statistics
- 2.9 billion monthly active users make Facebook one of the largest talent pools globally.
- 67% of recruiters use Facebook for hiring, particularly for frontline and hourly positions.
- Facebook job posts generate up to 29% of applications for small and mid-sized businesses.
- 79% of job seekers report using Facebook to search for job opportunities.
- Employer posts with employee stories on Facebook see 2x higher engagement compared to generic job listings.
- 60% of hiring managers review Facebook profiles to assess candidate fit.
- Facebook Groups serve as recruiting hubs, with thousands of niche job communities in tech, healthcare, and skilled trades.
- Paid Facebook recruitment ads can reduce cost-per-application by up to 30% compared to traditional job boards.
Impact of Social Media Recruitment Across Generations
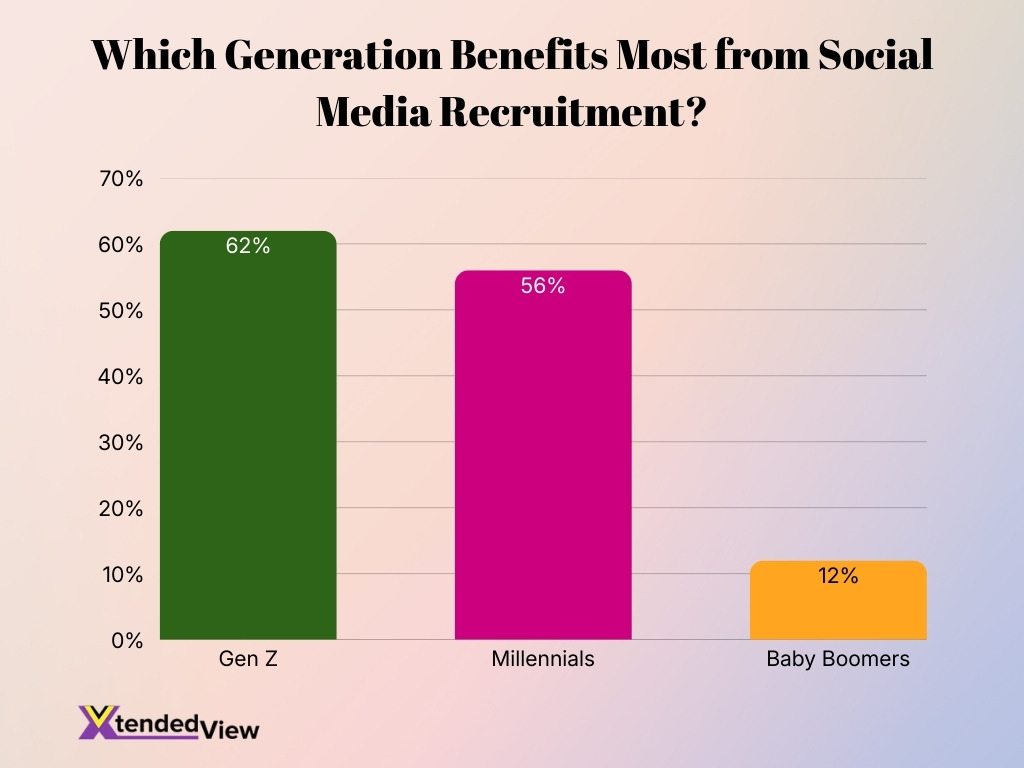
- Gen Z leads adoption, with 62% benefiting from social media recruitment, highlighting their strong preference for digital-first job searching.
- Millennials follow closely, with 56% using social platforms for career opportunities, showing continued reliance on online networking.
- Baby Boomers show limited engagement, with only 12% benefiting from social media hiring channels.
- The data indicates a strong generational shift toward digital recruitment, led primarily by younger professionals.
- Employers targeting Gen Z and Millennials can achieve higher hiring efficiency by prioritizing LinkedIn, Instagram, and emerging platforms.
- The low participation rate among Baby Boomers suggests that traditional recruitment methods still play a key role for older workers.
- Overall, social media recruitment is most effective among digitally native generations, with over 60%+ engagement from Gen Z alone.
Emerging Platforms Statistics
- TikTok reached 1.59 billion monthly active users globally in early 2025.
- 23% of recruiters adopted TikTok for talent sourcing by 2026.
- Instagram Reels achieve 1.23% average engagement rate, outperforming photo posts.
- Reddit’s daily active users grew to 443.8 million in Q3 2025.
- Discord monthly active users projected at 259.2 million in 2025, up 13.8% YoY.
- 51% of people are more likely to share employer branding videos.
- Snapchat reaches 75% of 13-34 year olds in over 25 countries.
- Threads hit 400 million monthly active users by Q3 2025.
- Bluesky reached 40 million registered users in late 2025.
Job Seeker Behavior Statistics
- 86% of job seekers use social media in their employment search.
- 79% of job seekers seek job opportunities via social platforms.
- 75% of new hires announce job changes on LinkedIn, boosting visibility.
- 62% of job seekers evaluate an employer’s social presence before applying.
- Many job seekers use mobile social feeds for job alerts and research.
- Positive social content increases job application rates.
- Candidates engage with culture-related posts more than simple job ads.
- Job seekers often view employer branding content to assess fit and values.
Age-Wise Social Media Usage in Job Search
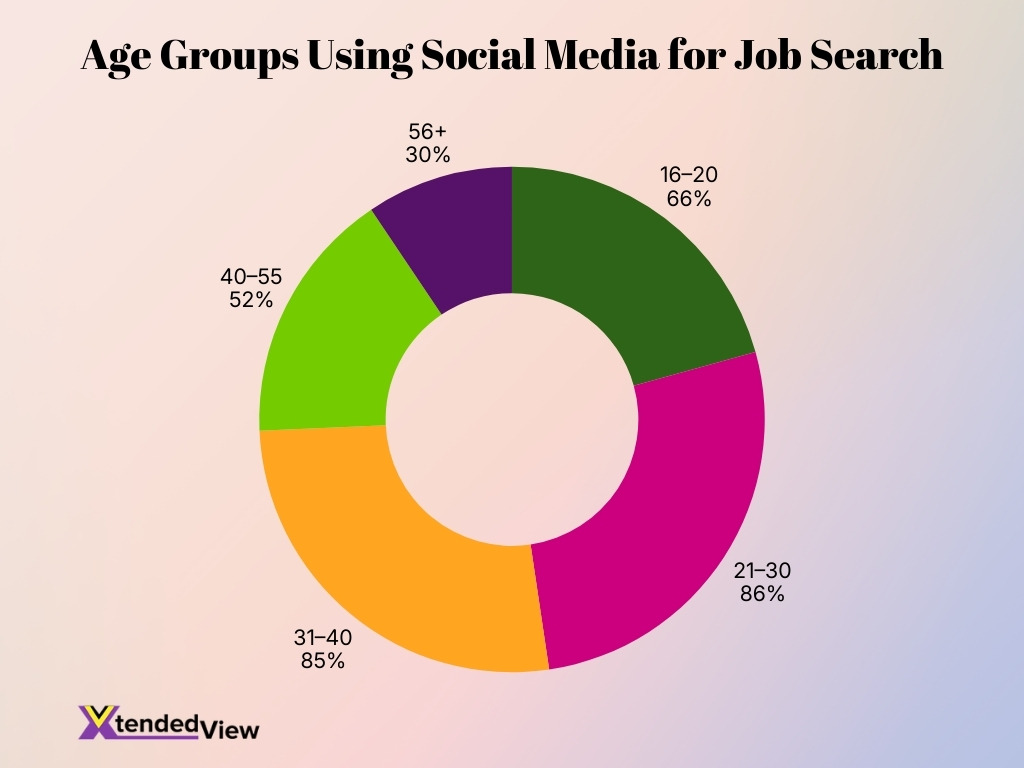
- Young professionals aged 21–30 lead adoption, with 86% using social media platforms to find job opportunities, making this the most active group.
- Job seekers aged 31–40 closely follow, showing strong engagement at 85%, reflecting high reliance on digital networking and recruitment tools.
- Students and early entrants aged 16–20 demonstrate notable participation, with 66% using social media for job searches and career exploration.
- Mid-career professionals aged 40–55 show moderate usage, with only 52% relying on social platforms for employment opportunities.
- Older job seekers aged 56+ record the lowest adoption, with just 30% using social media for job hunting, indicating a preference for traditional methods.
- Overall, social media job search usage peaks between ages 21 and 40, where adoption remains above 85%, highlighting the importance of digital recruitment for prime working-age groups.
- The data reveals a clear generational gap, with usage dropping by 56 percentage points from 86% (ages 21–30) to 30% (ages 56+), underscoring shifting digital behavior across age groups.
Passive Candidate Sourcing Statistics
- Passive candidates represent 70-75% of the global workforce.
- Only 30% of professionals actively seek jobs, leaving 70% as passive talent.
- 75% of the reachable talent market is passive, including career-informed professionals.
- Passive job-seekers comprise 73% of applicant pools for recruiters.
- Personalized LinkedIn InMails boost response rates by 15% for passive candidates.
- Referral hires from passive sourcing have 46% higher retention rates.
- Employee advocacy extends brand reach by 561% to engage passive talent.
- 89% of passive candidates evaluate employer brand before considering opportunities.
- Organizations targeting passive talent achieve 25% higher retention rates.
Screening Candidates on Social Media
- 70% of employers screen candidates’ social profiles during hiring decisions.
- 54% of employers have rejected candidates based on social media content.
- 60% of hiring managers review Facebook profiles for behavioral indicators.
- 57% of recruiters use LinkedIn profiles to verify work experience and credentials.
- Employers report that professional social presence positively influences hiring decisions in 44% of cases.
- In contrast, inappropriate content or discriminatory language leads to automatic rejection in over 50% of reviewed cases.
- Privacy and compliance training has increased among HR teams to reduce legal risk tied to social screening.
- Nearly 30% of candidates adjust privacy settings during job searches to manage employer visibility.
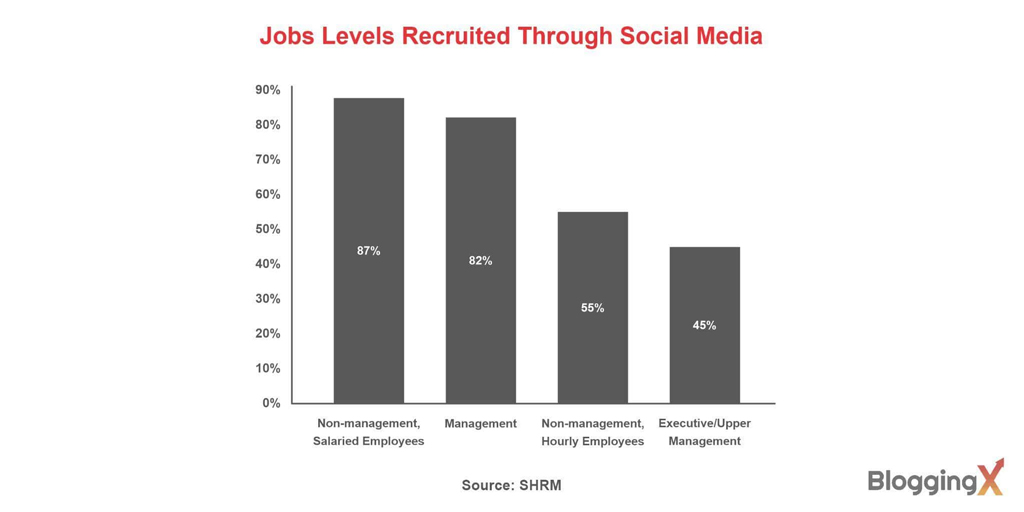
Social Media Recruitment by Job Level
- Non-management, salaried roles dominate social hiring, with 87% of these positions being recruited through social media, making them the most digitally sourced job category.
- Management-level hiring remains highly social-driven, as 82% of management roles are filled via social platforms, highlighting strong recruiter reliance on online networks.
- Hourly non-management employees show moderate social media adoption, with 55% of these hires coming through social channels, indicating room for growth in frontline recruitment.
- Executive and upper management roles rely least on social recruiting, at just 45%, reflecting continued preference for traditional and referral-based hiring methods.
- There is a clear decline in social media usage as job seniority increases, dropping from 87% at the salaried staff level to 45% at the executive level.
- Mid-level and operational roles benefit most from digital recruitment, as both salaried (87%) and management (82%) positions show consistently high social hiring rates.
- Senior leadership hiring remains more relationship-driven, with over 50% of executive roles still sourced outside social media platforms.
- Overall, social media proves most effective for high-volume hiring, especially for salaried and management roles where adoption exceeds 80%.
- The 42-point gap between salaried staff and executives (87% vs. 45%) highlights a significant opportunity for expanding social recruitment at the leadership level.
- Organizations investing in social recruiting strategies can maximize reach, particularly in roles with proven success rates above 80%.
Content Posting and Engagement Statistics
- Companies posting 3–5 times weekly on social media achieve ~12% more reach per post.
- Weekly posting on LinkedIn delivers 2x more engagement for recruiters.
- Employer branding videos generate up to 28% higher engagement when combined with user content.
- Employee-generated content drives 8x more engagement than brand posts.
- Posts with images on LinkedIn receive 5.2x more impressions than text-only.
- 98% of LinkedIn posts with images get more comments in recruitment.
- 75% of job seekers consider employer social content before applying.
- Hashtag use on LinkedIn boosts post impressions by 29%.
- Strong social engagement cuts time-to-hire by an average of 12 days.
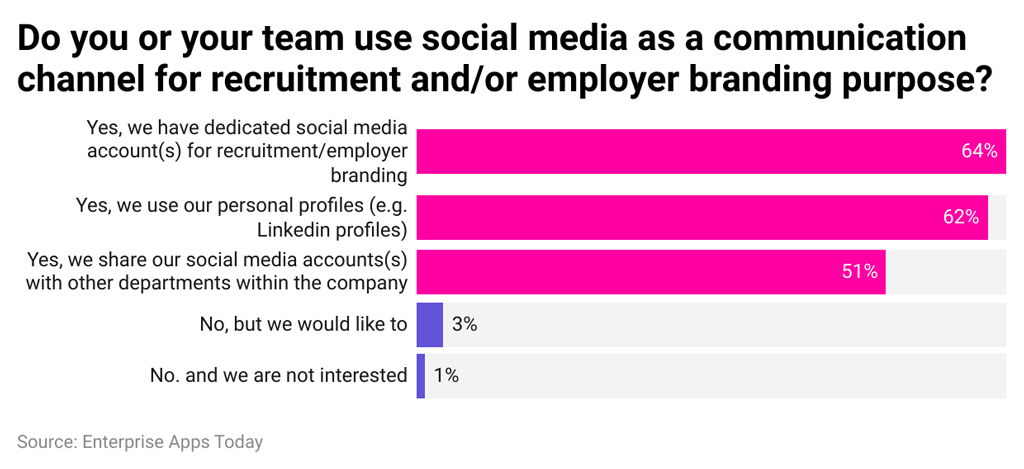
Social Media Use in Recruitment and Employer Branding
- 64% of organizations use dedicated social media accounts specifically for recruitment and employer branding, showing a strong focus on specialized talent outreach.
- 62% of recruiters and teams rely on personal profiles (such as LinkedIn), highlighting the importance of individual branding in hiring strategies.
- 51% of companies share their recruitment social media accounts with other internal departments, indicating cross-functional collaboration in employer branding.
- Only 3% of organizations currently do not use social media but plan to adopt it, suggesting that most employers have already embraced social recruiting.
- Just 1% of companies are not interested in using social media for recruitment, confirming that resistance to social hiring channels is extremely low.
- Overall, more than half of employers (50%+) actively integrate social media into their recruitment and branding efforts, making it a core hiring channel.
- The high adoption of both dedicated accounts (64%) and personal profiles (62%) reflects a dual-channel strategy used by many organizations to attract talent.
- The strong usage rates indicate that social media is no longer optional, but a standard tool for modern recruitment and employer branding.
Success Rates and ROI
- Companies that use social media recruiting report up to 50% lower cost-per-hire compared to traditional job boards.
- 42% of recruiters say social recruiting improves the quality of candidates they hire.
- Organizations with strong employer brands on social platforms see 50% more qualified applicants.
- Social recruiting reduces time-to-hire by an average of 20%, particularly for mid-level roles.
- 70% of hiring managers say social media helps them make better hiring decisions through improved candidate insights.
- Employee referral programs amplified via social media generate hires that stay 45% longer than other hires.
- Recruitment marketing campaigns on LinkedIn deliver a 2–3x higher conversion rate than standalone job board listings.
- Companies actively investing in employer branding on social platforms report 28% lower turnover rates.
Budget Allocation for Social Recruitment
- 60% of talent acquisition teams increased their social recruiting budgets between 2024 and 2026.
- Recruitment marketing budgets now allocate over 25% specifically to social media advertising and content.
- Small businesses dedicate an average of $1,500–$3,000 per month to social recruitment campaigns.
- Enterprise organizations spend $100,000+ annually on LinkedIn talent solutions subscriptions.
- 48% of HR leaders plan further budget increases for paid social recruiting in 2026.
- Paid social ads reduce cost-per-click by up to 30% when optimized with audience targeting tools.
- Video recruitment ads receive 34% more budget allocation compared to static image ads.
- Companies investing in analytics tools for social recruiting see 18% better budget efficiency year over year.
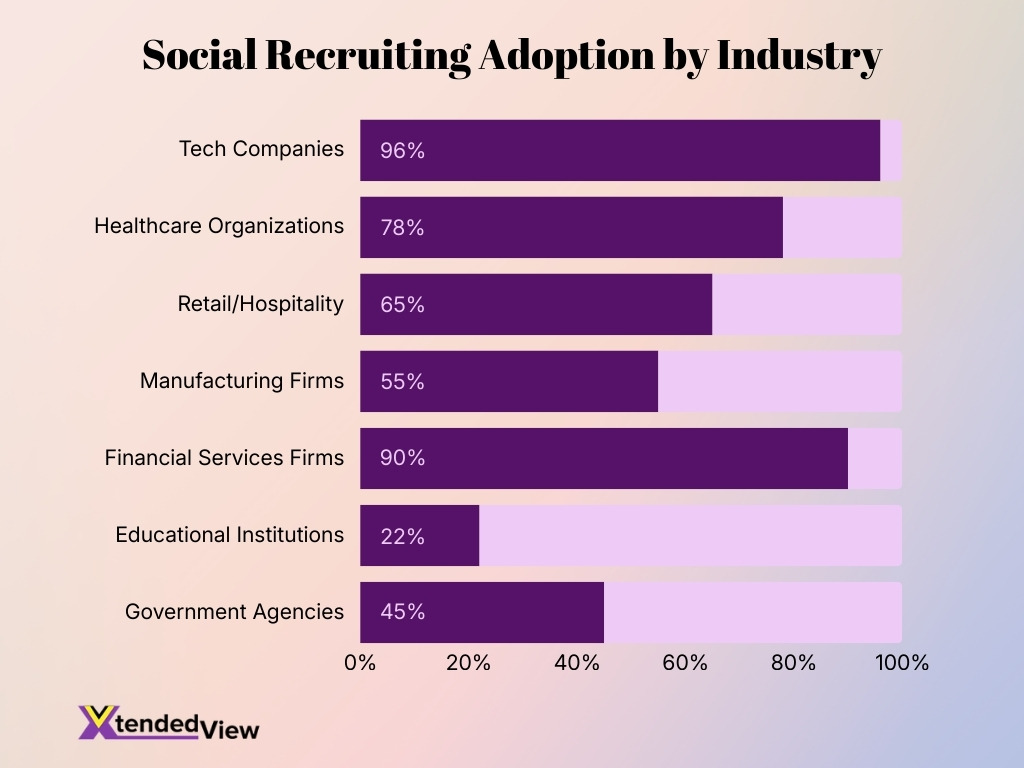
Industry Variations in Usage
- Tech companies lead social recruiting adoption at over 96% usage rates.
- Healthcare organizations report 78% reliance on social media for candidate sourcing, especially for nursing roles.
- Retail and hospitality brands rely heavily on Facebook and Instagram, with 65% of roles promoted via social platforms.
- Manufacturing firms report 55% adoption, reflecting slower digital recruitment transformation.
- Financial services firms use LinkedIn at 90% adoption rates for mid- to senior-level hiring.
- Educational institutions increased social recruitment spending by 22% year over year to reach Gen Z candidates.
- Government agencies report 45% utilization, largely focused on employer branding rather than direct sourcing.
- Startups are 2x more likely than large enterprises to experiment with TikTok recruiting campaigns.
Company Size and Recruitment Statistics
- 89% of large enterprises (1,000+ employees) use dedicated social recruiting teams.
- Mid-sized companies (100–999 employees) report 74% adoption of formal social hiring strategies.
- Small businesses rely on Facebook for hiring at a rate of 67%, particularly for hourly roles.
- Companies with fewer than 50 employees allocate 15–20% of recruitment budgets to social media.
- Enterprises using LinkedIn Recruiter report 20% faster hiring cycles than those using basic job posting tools.
- Small firms see 35% higher engagement rates on social posts due to more localized audiences.
- Global corporations use social media across multiple language markets, increasing candidate reach by 40%.
- Remote-first companies report 30% higher reliance on social platforms for cross-border hiring.
Challenges in Social Recruiting
- 37% of recruiters cite difficulty measuring ROI from social campaigns.
- 33% of HR leaders report compliance and privacy concerns when screening social profiles.
- Content saturation reduces organic reach, with average engagement rates declining by 12% year over year.
- 29% of employers struggle to convert social engagement into completed applications.
- Algorithm changes on major platforms affect visibility for over 40% of recruiters.
- Talent shortages in specialized industries increase competition on LinkedIn, where recruiter InMail volume grew over 20% annually.
- Employer brand inconsistency across platforms impacts application quality in 25% of cases.
- 45% of recruiters say creating consistent, high-quality content remains their top operational challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
91% of employers use social media in their talent acquisition and hiring strategies.
About 86% of job seekers use social media to explore jobs and job-related content.
Roughly 92% of recruiters leverage social media platforms like LinkedIn, Instagram, and TikTok to source talent.
About 98% of organizations now use social media to support hiring and enhance employer brand awareness.
Around 78% of recruiters have reported successfully making hires using social media recruitment tactics.
Conclusion
Social media recruitment is no longer optional; it is a core component of modern talent acquisition strategy. From LinkedIn’s billion-member ecosystem to TikTok’s rapid growth among Gen Z candidates, employers now compete in highly visible digital spaces. At the same time, ROI pressures, privacy regulations, and platform algorithm changes require smarter budget allocation and performance tracking.
For U.S. employers and global organizations alike, the data shows clear direction: companies that invest in strong employer branding, targeted outreach, and analytics-driven decision-making consistently see better hiring outcomes and lower costs. As social platforms continue evolving, recruitment teams that adapt quickly will secure stronger pipelines and long-term talent advantages.


