Social media now touches nearly every corner of daily life in the United States and globally. With over 4.9 billion people using social platforms and the average person spending more than two hours daily online, its reach continues to grow year after year. While these platforms offer community and information, their impact on mental health, especially among teens and young adults, is under intense scrutiny by researchers, policymakers, and families.
From social comparison pressures to sleep disruption, emerging data paint a complex picture of how social media shapes emotional well-being. Dive into this data story to understand the latest trends and statistics.
Editor’s Choice
- 4.9+ billion people globally use social media as of 2025, the highest level ever recorded.
- Roughly 95% of young people ages 13–17 report using at least one social platform.
- Teens using social media 5+ hours daily are twice as likely to go to bed later than their peers.
- Over 210 million people worldwide (~4.7%) may struggle with problematic social media engagement.
- 23% of all users have sought mental health advice on social platforms, 55% of Gen Z turn there too.
- Multiple studies link heavy social media use to increased rates of anxiety and depression.
- Research shows social media can exacerbate sleep problems, particularly among teens.
Recent Developments
- Major tech companies like Meta and Google face lawsuits alleging their platforms were designed to be addictive, with implications for youth mental health.
- 86% of Americans want tech companies held responsible for predatory features linked to addiction.
- New state laws require warning labels on popular social apps to educate families about potential risks.
- Legal testimony has highlighted internal debates about well-being recommendations within major tech firms.
- Some research challenges the narrative that digital screen time alone increases mental health symptoms, arguing that context matters more than hours spent.
- Global health bodies are emphasizing digital well-being campaigns to counter rising mental health concerns tied to screen use.
- Several landmark studies in 2026 highlight nuanced psychological patterns tied to algorithmic content exposure.
Overview of Social Media Mental Health Statistics
- Up to 95% of U.S. teens (13–17) use social media platforms regularly.
- Global social media users exceeded 5.42 billion in 2025.
- Roughly 17% of the world’s population shows signs of problematic engagement with social platforms.
- The average daily social media use among all users is nearly 3 hours.
- About 40% of adults report that social media makes them feel more isolated or lonely.
- Heavy use correlates with higher self-reported rates of anxiety and depression in multiple surveys.
- Nearly one-third of teens report “almost constant” social platform use.
- Young people who regularly compare themselves online report greater social isolation.
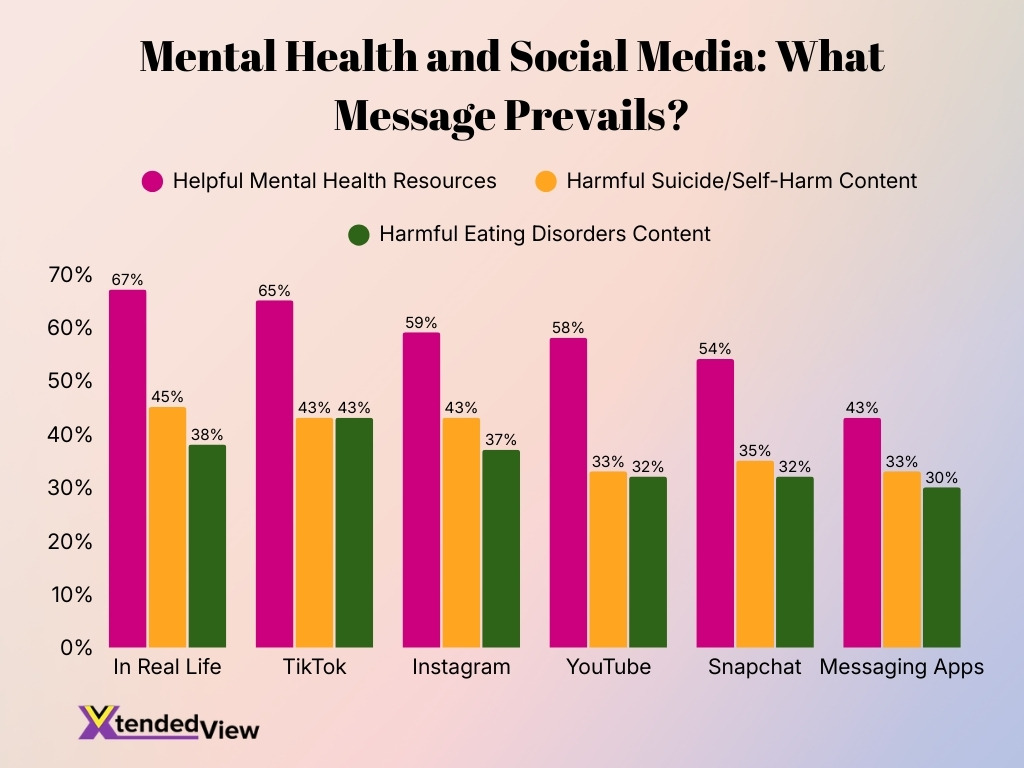
Mental Health Content Exposure Among U.S. Girls on Social Media
- In real life, shows the highest exposure to **helpful mental health resources at 67%, compared to 45% encountering harmful self-harm content and 38% seeing eating disorder-related content.
- TikTok provides supportive mental health information to 65% of users, while 43% are exposed to suicide or self-harm content, and another 43% encounter eating disorder-related material.
- Instagram reaches 59% of girls with helpful mental health resources, but 43% still report exposure to harmful self-harm content and 37% to eating disorder content.
- YouTube delivers positive mental health information to 58% of users, alongside 33% exposure to self-harm content and 32% to eating disorder-related posts.
- Snapchat offers helpful mental health content to 54% of girls, while 35% report seeing harmful self-harm material, and 32% encounter eating disorder content.
- Messaging apps show the lowest level of positive exposure at 43%, yet still expose 33% of users to self-harm content and 30% to eating disorder-related information.
Time Spent on Social Media and Mental Health Outcomes
- People spending 3+ hours daily on social media are twice as likely to experience poor mental health outcomes.
- Teens using social media for 3+ hours daily are 70% more likely to fall asleep after 11 PM.
- Heavy users aged 16–24 show increased rates of anxiety and depression linked to social media use.
- Global average daily social media engagement is 2 hours 21 minutes.
- Very high users (5+ hours) report poorer sleep quality and shorter duration.
- 48% of adolescents use social media 3+ hours daily, linked to 2x higher psychological distress.
- Passive scrolling on social media correlates with elevated depressive symptoms more than active use.
- 40% of depressed youth exhibit problematic social media use, worsening anxiety, and suicidal thoughts.
- Teens spending 5+ hours daily on social media face a 2.3x higher risk of depressive symptoms.
- Social media use exceeding 3 hours daily doubles anxiety/depression risk in teens.
Problematic and Addictive Social Media Use Statistics
- An estimated 210 million people worldwide show signs of social media addiction or problematic use.
- 41% of teens report feeling addicted to social media.
- Nearly 1 in 3 adolescents say they use social media almost constantly.
- Teens who use social media more than 3 hours per day face double the risk of poor mental health outcomes.
- Compulsive checking behaviors correlate with changes in reward sensitivity in early adolescents.
- About 44% of Gen Z users say they feel anxious when they cannot access their social accounts.
- 58% of teens feel pressure to respond immediately to notifications.
- Young adults ages 18–24 report the highest levels of self-identified social media dependency.
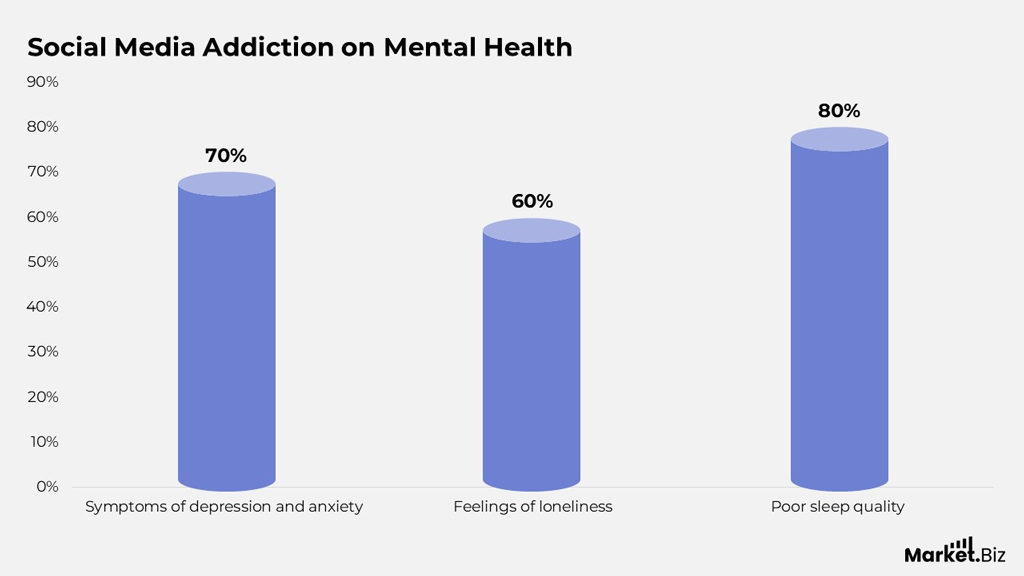
Impact of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health
- 80% of individuals report experiencing poor sleep quality, making it the most significant mental health impact linked to social media addiction.
- Around 70% of users face symptoms of depression and anxiety, highlighting a strong correlation between excessive social media use and emotional distress.
- Approximately 60% struggle with feelings of loneliness, indicating that high online engagement does not necessarily translate to real-world social connection.
- The data suggests that sleep disruption is the leading consequence, followed by mental health disorders and social isolation effects.
Social Media and Depression Statistics
- Adolescents spending over 3 hours daily on social media have a 13% higher risk of depressive symptoms.
- 42% of high school students felt persistent sadness or hopelessness, per CDC data.
- Girls report depressive symptoms from social media at twice the rate of boys.
- Heavy users (5+ hours/day) show 38% rate of clinical depression symptoms.
- Frequent online social comparison boosts depression scores by up to 30% in teens.
- Passive scrolling correlates 2.5x more strongly with depressed mood than active posting.
- Teens cutting social media to 30 minutes/day saw depression drop by 25% in 3 weeks.
- LGBTQ+ youth face 54% depression rates, with online communities aiding 40% as support.
- 40% of depressed teens link suicidal thoughts to problematic social media use.
Social Media and Anxiety Statistics
- 36% of teens say social media makes them feel anxious about their lives.
- Young adults ages 18–29 report the highest anxiety levels associated with online comparison.
- Image-based platforms rank highest for anxiety impact among major platforms.
- Nearly 60% of Gen Z users feel stressed if posts receive fewer likes or comments than expected.
- Constant notification exposure increases physiological stress responses.
- Adolescents experiencing cyberbullying report significantly higher anxiety scores.
- About 70% of teens report feeling left out after seeing posts about social gatherings.
- Daily social comparison correlates with higher social anxiety symptoms.
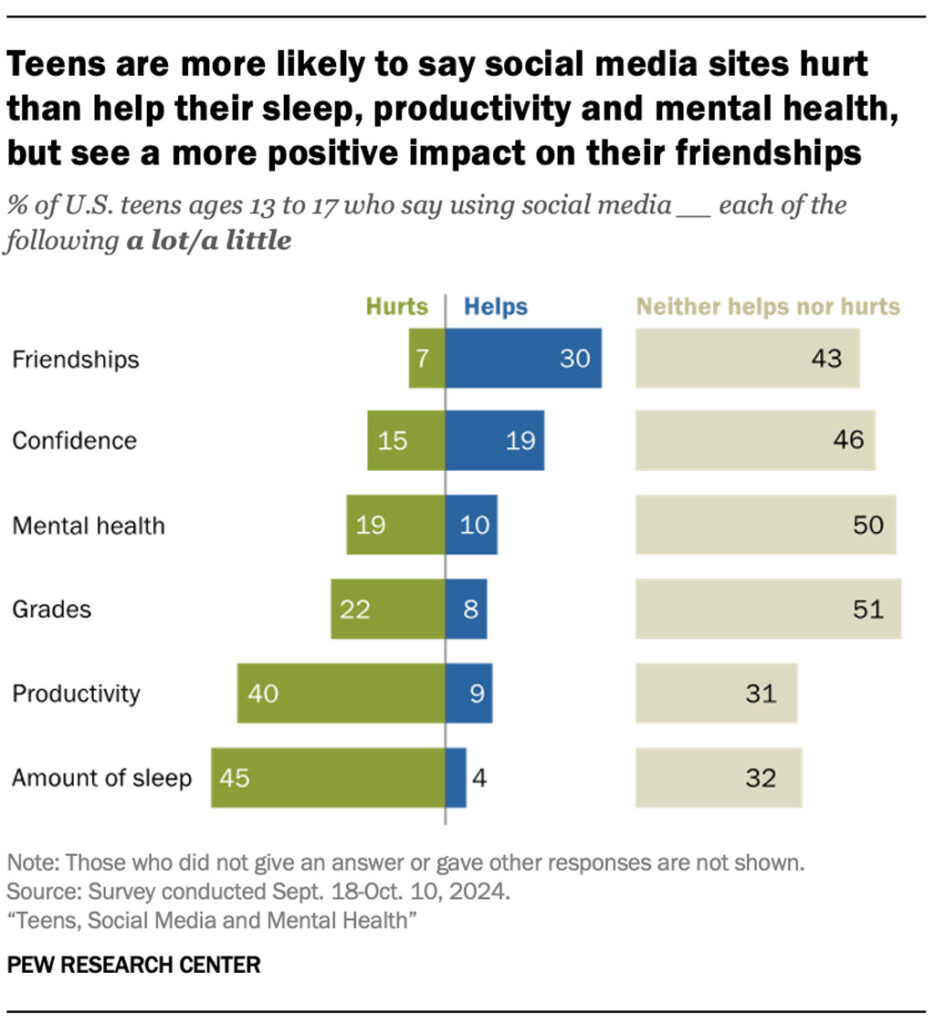
How Social Media Impacts U.S. Teens’ Sleep, Grades, and Mental Health
- A significant 45% of teens say social media hurts their amount of sleep, while only 4% believe it helps, making sleep the most negatively impacted area.
- 40% of teens report that social media hurts their productivity, compared to just 9% who say it helps.
- When it comes to grades, 22% say social media hurts academic performance, while only 8% see a positive impact.
- Regarding mental health, 19% of teens say social media hurts, while just 10% believe it helps, with 50% saying it neither helps nor hurts.
- Teens are somewhat more divided on confidence, where 19% say social media helps and 15% say it hurts, though 46% report no major impact.
- Friendships stand out as the most positively viewed category, with 30% of teens saying social media helps, compared to only 7% who say it hurts, while 43% report neutral effects.
- In most categories, including mental health (50%) and grades (51%), about half of teens say social media neither helps nor hurts, indicating mixed or moderate overall effects.
Social Media, Stress, and Emotional Distress Statistics
- 48% of teens use social media for 3+ hours daily, linking to higher psychological distress.
- 43.7% of adolescents experience moderate to severe psychological distress, rising to 54% in females.
- Heavy social media use doubles the odds of severe psychological distress (OR: 2.01) in adolescents.
- 45% of teen girls feel social media hurts their mental health, vs. 14% of boys.
- 39% of teens say social media makes them feel overwhelmed by drama.
- 41% of high-use teens rate their mental health as poor or very poor.
- 35% of teens are online almost constantly, tying to increased stress.
- 11% of adolescents show problematic social media behavior with negative emotional effects.
- 20 minutes of social media raises cortisol levels more in depressed adolescents.
Social Media and Loneliness or Social Isolation Statistics
- Young adults (19-32) using social media ≥58 times weekly have 3.4x higher odds of high social isolation.
- Heaviest social media users (≥30 hours/week) among college students are 38% more likely to feel lonely.
- Over half of U.S. college students report loneliness, exacerbated by heavy social media use, like 16+ hours weekly.
- Passive social media use on platforms like YouTube and Reddit links to above-average loneliness levels in young adults.
- 9.8% of social media users who primarily follow influencers feel more isolated.
- LGBTQ+ youth connecting online report reduced isolation and increased well-being via supportive communities.
- Older adults show a negative correlation between social media use and loneliness, unlike younger users.
- 40% of young adults aged 18-22 feel addicted to social media, heightening loneliness risks.
- Girls experience 17% high social isolation rates with elevated social media use versus 10% in boys.
Social Media and Self-Esteem or Body Image Statistics
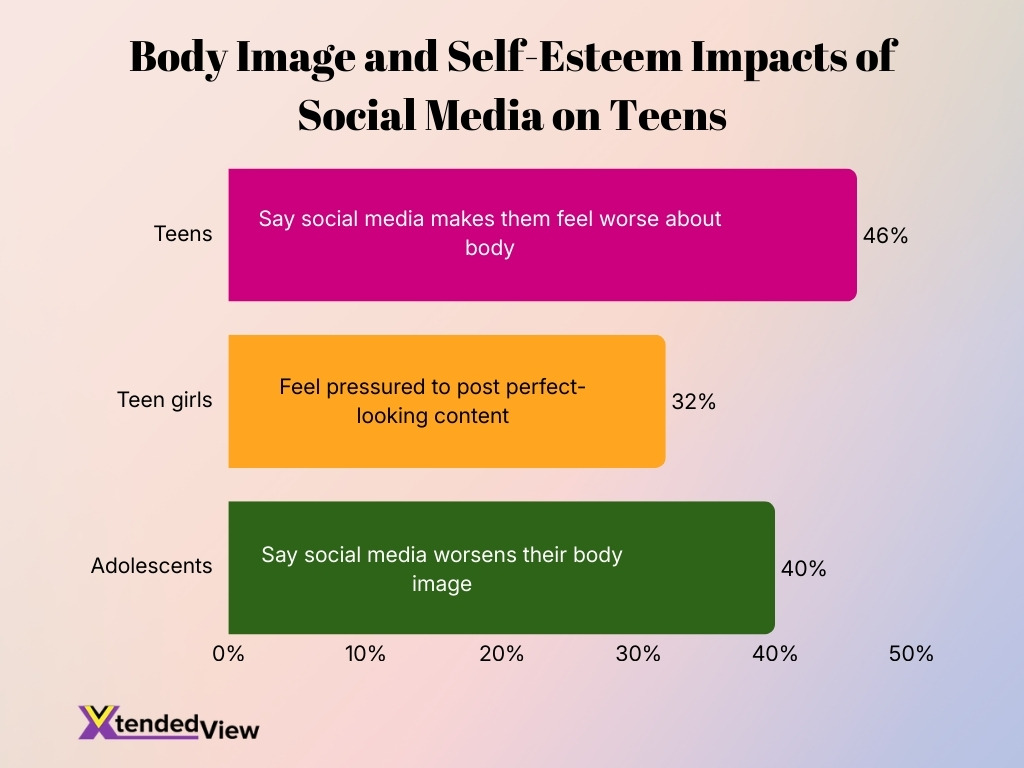
- Nearly 46% of teens say social media makes them feel worse about their body image.
- Image-based platforms rank among the most harmful for body perception among young women.
- Teen girls spending >3 hours daily on image-focused platforms face an increased risk of low self-esteem.
- Photo editing and filter use are linked to increased body dissatisfaction.
- About 32% of teen girls feel pressured to post perfect-looking content.
- Social comparison predicts lower self-worth scores in college students.
- Exposure to appearance-focused content boosts negative body perception.
- Positive representation and body-neutral content improve self-esteem metrics.
- 40% of adolescents report that social media worsens their body image.
- Girls using social media 3+ hours/day are 2x more likely to be dissatisfied with their bodies.
Social Media and Sleep Problems Statistics
- Teens spending 3+ hours daily on social media are 70% more likely to fall asleep after 11 p.m. on school nights.
- Adolescents using devices before bed average 7.3 hours of sleep per night.
- 72.7% of high school students get insufficient sleep on school nights.
- Very high social media users are 70% more likely to have trouble falling back asleep after waking.
- Blue light from screens significantly suppresses melatonin production in teens.
- 97% of adolescents use technology in the hour before sleep, worsening their quality of sleep.
- Heavy social media use links to 26% higher depressive symptoms in teen girls via sleep issues.
- Reducing social media to 30 minutes daily cuts insomnia symptoms by 14.5% in young adults.
- 43% of teen girls use social media over 3 hours daily, disrupting sleep.
- Social media addiction positively correlates with insomnia and depression in adolescents.
Cyberbullying and Online Harassment Statistics
- 16% of U.S. high school students experienced electronic bullying in the past year.
- Girls report cyberbullying at 18% vs. 14% for boys.
- Nearly 59% of U.S. teens have experienced at least one form of online harassment.
- Cyberbullying victims are more than twice as likely to report depression and anxiety symptoms.
- About 1 in 5 teens avoid social media temporarily due to harassment.
- LGBTQ+ youth report significantly higher rates of online harassment.
- Teens facing repeated online bullying report higher stress and lower academic performance.
- Schools implementing digital citizenship programs see measurable declines in cyberbullying incidents.
Social Media Usage and Mental Health Risk Among US Teens
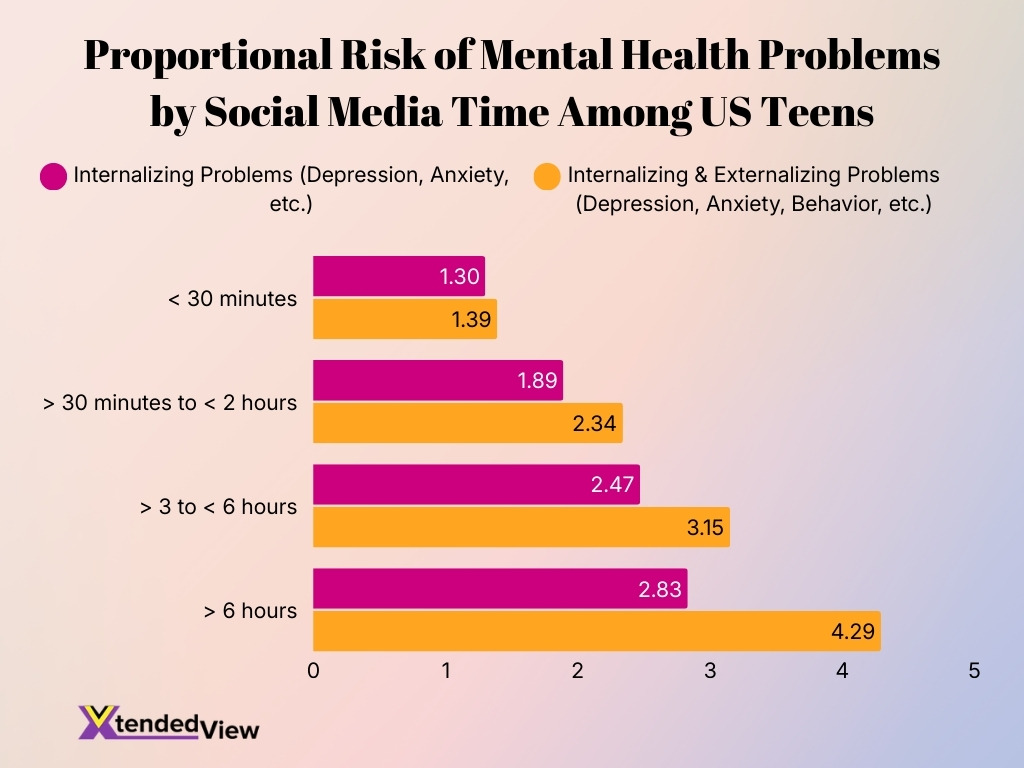
- Teens who use social media for less than 30 minutes per day show a proportional risk score of 1.30 for internalizing problems and 1.39 for combined internalizing and externalizing problems.
- Usage between more than 30 minutes and less than 2 hours per day increases the risk to 1.89 for internalizing issues and 2.34 for combined mental health problems.
- Teens spending more than 3 to less than 6 hours daily on social media face a significantly higher risk, with scores rising to 2.47 (internalizing) and 3.15 (internalizing and externalizing).
- Those using social media for more than 6 hours per day experience the highest proportional risk, reaching 2.83 for internalizing problems and a striking 4.29 for combined mental health issues.
- The data shows a clear dose-response relationship, where increased daily social media time is associated with progressively higher mental health risk levels.
- The steepest increase is observed in the >6 hours category, particularly for internalizing and externalizing problems, suggesting heightened vulnerability among heavy users.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Social Comparison Statistics
- Nearly 70% of teens sometimes feel excluded after seeing posts about events they did not attend.
- Young adults ages 18–29 report the highest FOMO levels among all age groups.
- Frequent social comparison links to higher life dissatisfaction scores by 20-30%.
- Teens who check social media hourly are 2x more likely to report FOMO-related anxiety.
- 56% of Gen Z users feel pressure to stay constantly updated on platforms.
- Social comparison is associated with 25% lower self-esteem among adolescent girls.
- Reduced social comparison behaviors lead to 15-20% measurable mood improvements.
- Influencer content exposure correlates with 18% reduced perceived life satisfaction.
- 69% of Gen Z experience FOMO from peer social media updates regularly.
Social Media and Suicidal Ideation or Self-Harm Statistics
- 22% of U.S. high school students seriously considered attempting suicide in 2021, linked to rising social media use.
- Girls reported 22.5% self-harm rates versus 9.5% for boys, with higher social media exposure among females.
- Cyberbullying victims face 4.2 times higher odds of suicidality compared to non-victims.
- 39% of LGBTQ+ youth seriously considered suicide in the past year, exacerbated by online harassment.
- 50% of teens exposed to self-harm content on social media over a study period, increasing NSSI urges.
- Adolescents using social media >3 hours daily have a 2.74 odds ratio for self-harm.
- 75% of high school students with frequent social media use reported higher suicide consideration and bullying.
- Cyberbullying triples (3.12 odds) suicide ideation risk more than in-person bullying (2.16).
- 12% of LGBTQ+ youth attempted suicide last year, tied to social media cyberbullying exposure.
Low Self-Esteem and Social Media Usage Among Teens
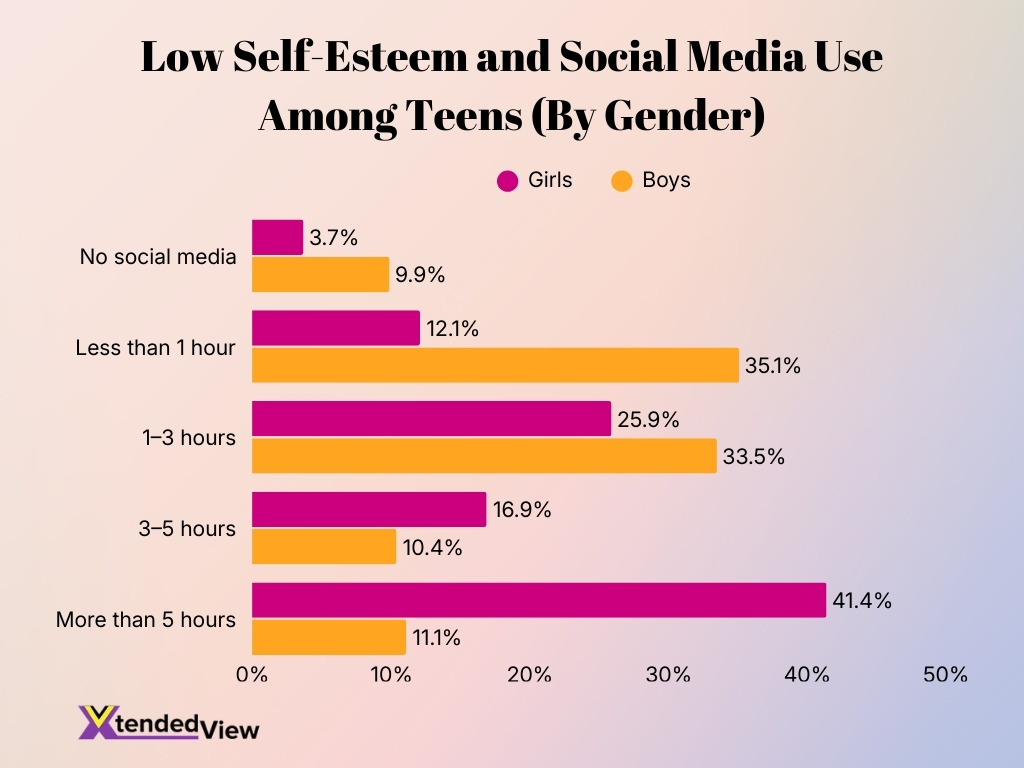
- 41.4% of girls who use social media for more than 5 hours daily report low self-esteem, the highest rate among all groups.
- Only 3.7% of girls with no social media use report low self-esteem, showing the lowest impact in this category.
- Among boys, the highest share of low self-esteem is seen in the less than 1 hour group at 35.1%.
- 33.5% of boys who spend 1–3 hours daily on social media report low self-esteem, indicating high vulnerability even at moderate usage.
- Boys with no social media use report 9.9% low self-esteem, nearly three times higher than girls in the same category.
- 25.9% of girls using social media for 1–3 hours experience low self-esteem, showing a steady rise with increased usage.
- In the 3–5 hours category, 16.9% of girls report low self-esteem, compared to only 10.4% of boys.
- Heavy usage impacts girls more strongly, with 41.4% vs 11.1% low self-esteem among those using social media for over 5 hours.
- Overall, girls show a stronger link between high social media use and low self-esteem than boys.
- The data suggests that excessive screen time is a key risk factor for teen mental well-being, especially for girls.
Social Media and Teen or Adolescent Mental Health Statistics
- 95% of teens use at least one social media platform.
- Nearly 46% of teens say social media worsens their body image.
- 1 in 3 teens (35%) use social media almost constantly.
- Teen girls report higher negative mental health effects from social media than boys (25% vs 14%).
- Teens spending >3 hours daily on social media face double the mental health risks, like depression and anxiety.
- 60% of high-use teens with low parental monitoring report poor mental health, vs 25% with strong monitoring.
- 52% of teens feel social media provides support from peers, boosting self-esteem.
- Frequent social media users experience higher bullying victimization, linked to increased school absenteeism.
- 51% of U.S. teens spend at least 4 hours daily on social media, averaging 4.8 hours.
- 11% of adolescents show problematic social media use, with girls higher (13% vs 9% for boys).
Platform-Specific Social Media Mental Health Statistics
- Instagram and TikTok users report 32% higher body dissatisfaction from image-focused content.
- Short-form video apps like TikTok exceed 60% U.S. teen usage rates.
- Snapchat users experience 25% more social comparison pressure than Facebook peers.
- YouTube leads with 93% usage among teens, daily for 76%.
- Facebook teen usage has dropped to under 33% daily.
- Image platforms correlate with 40% stronger anxiety links vs. text-based ones.
- Algorithm-driven feeds extend sessions by 28% over traditional.
- Platforms with mental health tools see 85% higher engagement rates.
- TikTok algorithms boost teen screen time to 107 minutes daily average.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
About 36% of teens report using major social media platforms almost constantly.
Over 11% of adolescents display problematic social media use, with girls at 13% and boys at 9%.
Approximately 77% of teens report that curated perfection on social media affects their body image and self-esteem negatively.
After one week off social media, anxiety symptoms dropped by 16.1%, and depression symptoms dropped by 24.8%.
Nearly 40% of adults say social media makes them feel lonely or isolated.
Conclusion
Social media now shapes how young people communicate, compare, and cope. The data show clear associations between heavy use and rising rates of anxiety, depression, sleep disruption, and emotional distress, particularly among teens and young women. At the same time, social platforms can foster connection, peer support, and access to mental health resources when used intentionally.
For families, educators, and policymakers in the United States, the message is clear: context, moderation, and digital literacy matter more than ever. As research evolves and beyond, stakeholders must balance innovation with responsibility to protect youth well-being while preserving the benefits of online connection.