Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide and has broad implications for personal identity and market growth. For example, in the U.S., many adults invest in prevention and restoration services as hair thinning becomes more visible in work and social settings. In the global medical device and cosmetic industries, rising hair loss rates drive innovation in diagnostics and treatments.
Editor’s Choice
Here are seven standout statistics that highlight major aspects of hair loss in 2025:
- 85% of men will experience some form of hair loss during their lifetime.
- 33% of women will face hair loss at some point.
- By age 35, about 65% of men notice some level of hair loss.
- The global alopecia market is projected to reach $11.6 billion in 2025.
- A cross‑sectional dataset of over 1 million users found 86.4% reported visible hair loss (43.7% mild, 31.6% moderate, 11.2% severe).
- Women aged 18‑65: 23% say their hair has gotten thinner, compared with 18% of men.
- In a phase‑2 trial of the drug candidate PP405, 31% of men achieved >20% increased hair density in 8 weeks vs 0% in placebo.
Recent Developments
- Researchers at the UVA School of Medicine discovered that stem cells in the upper and middle parts of hair follicles play an essential role in hair growth.
- A topical candidate, ET‑02, for androgenetic alopecia showed six times the hair growth of placebo within just one month.
- A new study suggests a naturally occurring sugar, deoxyribose, may stimulate hair regrowth by boosting blood vessel formation in follicles.
- By 2025, approximately 30% of hair loss treatments are expected to include stem cell therapy.
- AI‑based diagnostic platforms captured a dataset of 1,009,998 users (2020‑2024) showing visible hair loss in 86.4% of respondents.
- The market for hair thinning treatments grew from $1.51 billion in 2024 to a projected $1.64 billion in 2025.
- Clinical science is shifting from treating symptoms (thinning hair) to restoring dormancy in follicles by targeting core biological pathways.
Key Hair Loss Statistics
- An adult scalp typically has 80,000‑120,000 hairs.
- It is considered normal to shed about 50‑100 hairs per day.
- Around 85% of men and 33% of women will experience hair loss at some point.
- By age 30, 25% of men and 12% of women experience noticeable hair loss.
- By age 50, about 50% of men and 25% of women experience significant hair loss.
- Approximately 70% of hair loss cases have a genetic predisposition.
- The global alopecia treatment market was valued at $3.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $3.62 billion in 2025.
- In a dataset of 1 million participants, 43.7% reported mild hair loss, 31.6% moderate, and 11.2% severe.
- 23% of women aged 18‑65 say their hair is thinner vs 18% of men in the same age span.
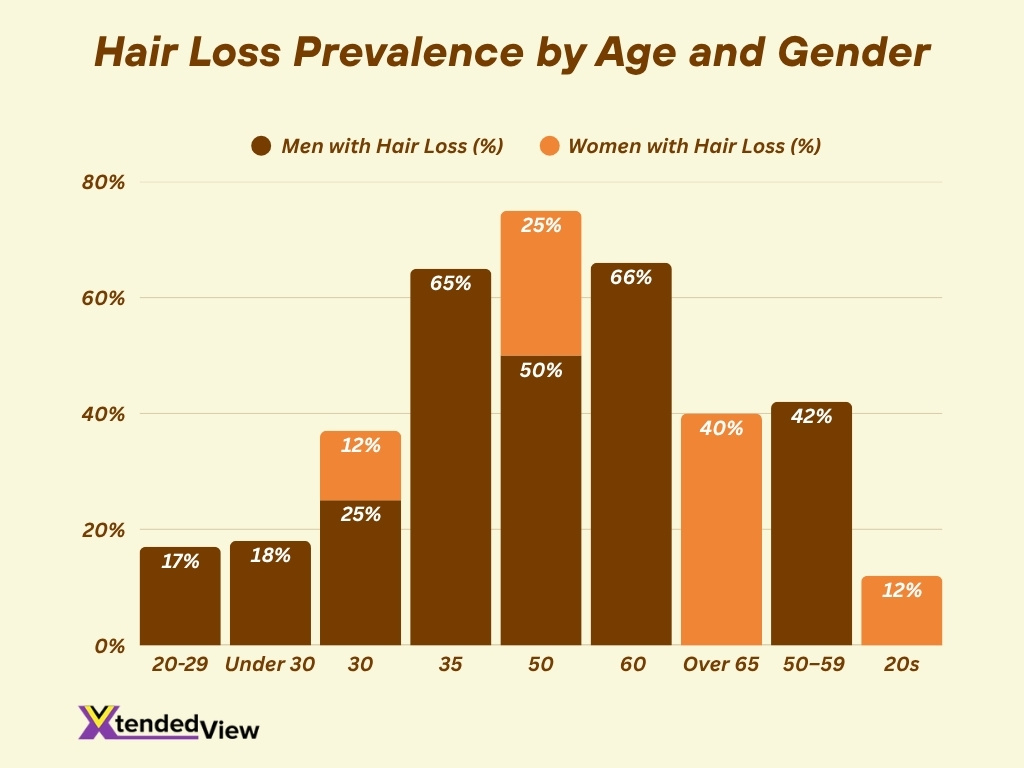
Hair Loss by Age Group
- By age 30, 25% of men and 12% of women experience noticeable hair loss.
- By age 35, about 65% of men notice some level of hair loss.
- By age 50, about 50% of men and 25% of women experience significant hair loss.
- By age 60, two-thirds of men are either bald or have a balding pattern.
- Among women over 65, approximately 40% show signs of visible thinning.
- 17% of men aged 20–29 already report mild hair loss.
- In one dataset (1M+ users), men aged 30–39 had the highest visible hair loss rate at 36.8%.
- 18% of individuals under 30 report some level of hair shedding due to stress or environmental factors.
- The onset of female pattern baldness typically begins in the late 30s or early 40s, but 12% of women report it starting in their 20s.
- Severity of hair loss increases with each decade, with 42% of men aged 50–59 experiencing moderate to severe hair loss.
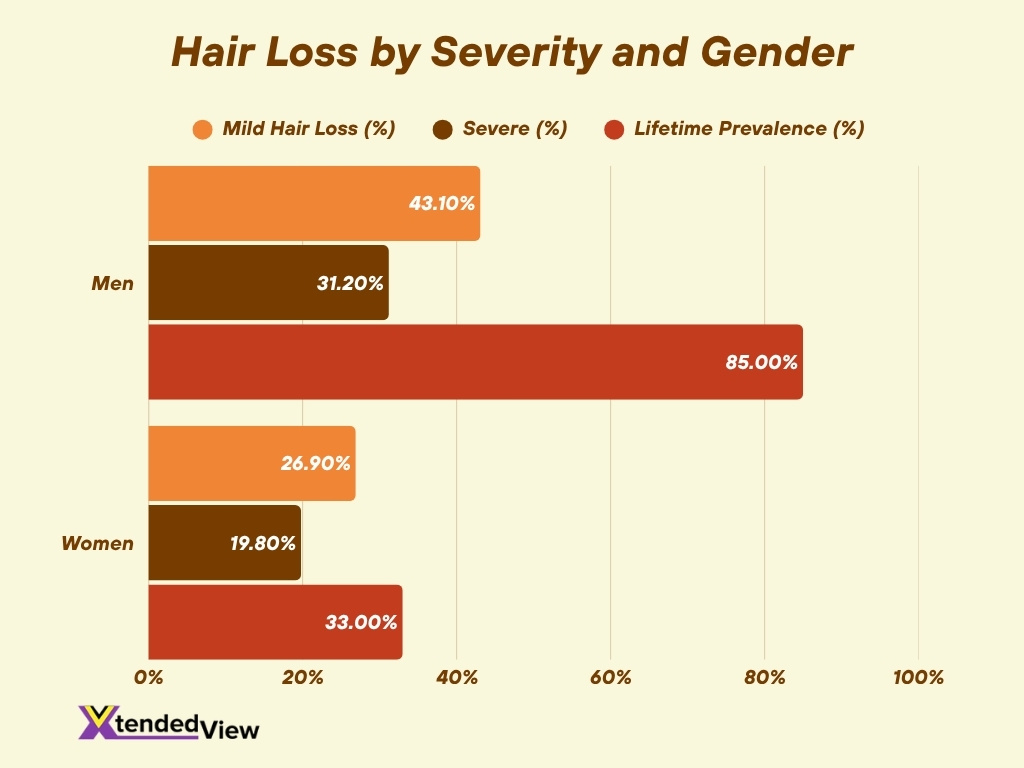
Hair Loss by Gender
- 85% of men will experience some form of hair loss during their lifetime.
- 33% of women will also face hair loss at some point.
- Male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) accounts for 95% of hair loss in men.
- Women experience a more diffuse thinning pattern, while men usually develop receding hairlines and vertex baldness.
- In a study of 1 million+ users, 43.1% of men reported mild hair loss vs 26.9% of women.
- 31.2% of men in the sample had moderate to severe hair loss compared to 19.8% of women.
- Postmenopausal women are more prone to hair thinning, with 50% of women over 65 affected.
- Hair loss in women often peaks after pregnancy or during hormonal changes such as perimenopause.
- More men than women seek clinical treatments or transplants, but the gap is narrowing due to growing awareness and acceptance among women.
- Women are more likely to report emotional distress, while men tend to normalize or conceal their hair loss.
Global Prevalence of Hair Loss
- Globally, 60% of men and 35% of women will experience noticeable hair loss in their lifetime.
- Approximately 1.5 billion people worldwide are currently experiencing some form of hair loss.
- Androgenetic alopecia affects nearly 50% of men and women globally by the age of 50.
- Alopecia Areata affects about 2% of the global population, with regional variation in burden and incidence.
- In Asia, prevalence among men aged 40–49 reaches up to 44%, with South Korea and Japan showing some of the highest rates.
- North America reports high lifetime prevalence, particularly in Caucasian males, at 65% by age 60.
- Africa has lower reported rates of male pattern baldness but higher prevalence of traction alopecia in women.
- A meta-analysis found that 42% of European men and 38% of South American men experience pattern hair loss by age 50.
- In the Middle East and India, rising stress, pollution, and poor diet are driving the earlier onset of hair loss in urban populations.
- Global studies show increasing trends of hair loss in both genders, attributed to lifestyle, environmental changes, and delayed treatment.
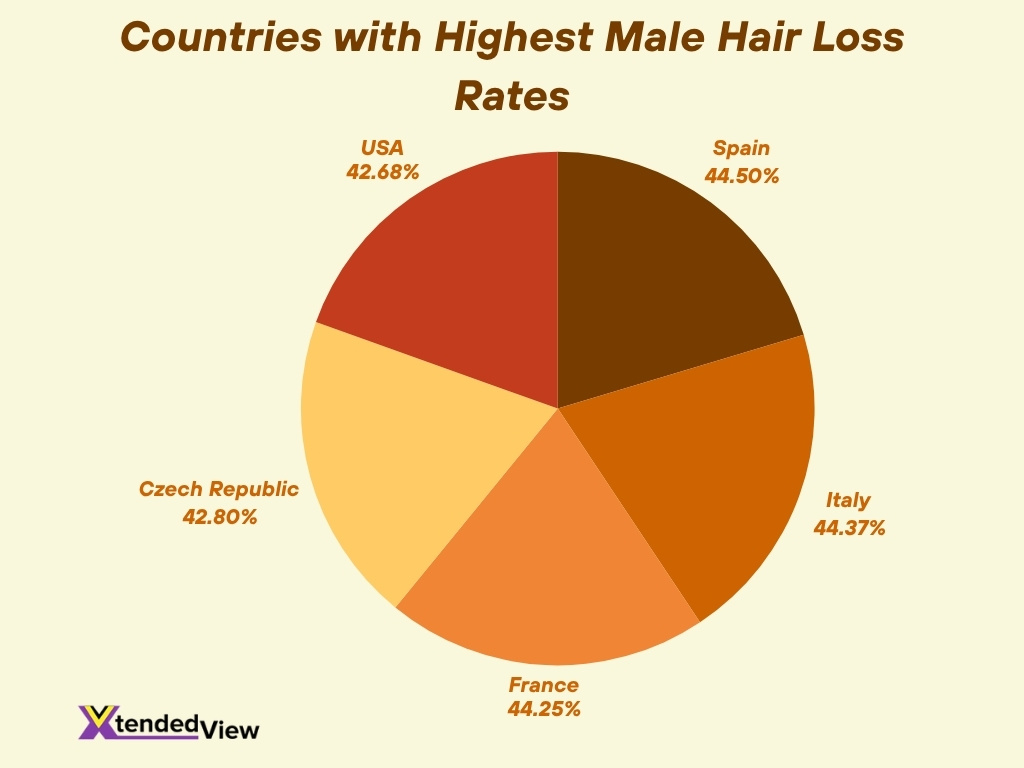
Hair Loss by Country or Region
- In the U.S., approximately 42.68% of adult men experience significant hair loss, placing it among the top five countries globally.
- Spain leads with 44.50% of men reportedly experiencing hair thinning or baldness.
- Italy follows closely at 44.37% of men affected.
- France reports 44.25% of its male population has significant hair loss.
- Among 46 countries studied, 28 had male pattern hair loss rates in the 30‑39.9% range, and 12 in the 40‑44.5% range.
- In the Czech Republic, nearly 42.8% of men are affected by baldness.
- Regions in Western Sub‑Saharan Africa saw rising incidence rates of Alopecia Areata, with an EAPC (estimated annual percentage change) of 0.07 between 1990 and 2019.
- In high-income North America, the DALY (disability adjusted life year) rate for alopecia areata fell from 1990 to 2019 (EAPC ‑0.29).
- Globally, while prevalence remains high, the biggest growth in disease burden for alopecia areata came from lower SDI (socio-demographic index) regions.
- Many country-level data focus on men; comprehensive female data by country are less widely reported.
Common Types of Hair Loss
- Androgenetic Alopecia (pattern hair loss) affects up to 50% of males and females over time.
- In men, androgenetic alopecia often begins after puberty and increases with age; for women, it frequently becomes noticeable after menopause.
- Telogen Effluvium is triggered by metabolic or hormonal stress. In a healthy scalp, 85% hair is in the anagen phase, 15% in the telogen phase, but under stress, the telogen proportion can increase markedly.
- Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss. Globally, incidence and DALY rates changed differently across regions between 1990 and 2019.
- Cicatricial (scarring) alopecia and hair loss due to infection or dermatologic disease are less common but potentially irreversible.
- Among an Indian clinical sample (24,595 patients), Telogen Effluvium: 40.70%, Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL): 22.09%, Alopecia Areata: 12.81%, Male Pattern Hair Loss (MPHL): 7.49%.
- In male hair loss cases, about 95% are attributed to androgenetic alopecia.
- The severity grades of pattern hair loss vary; one study found among UK men (52,874 sample) 31.6% no hair loss, 23.0% slight, 26.9% moderate, 18.5% severe.
- Identifying the type of hair loss is critical; treatments differ for pattern hair loss vs telogen effluvium, vs autoimmune causes.
Common Causes of Hair Loss
- A family history of hair loss remains the strongest predictor; genetic predisposition accounts for nearly 80‑90% of pattern hair loss risk.
- Hormonal factors like heightened sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) drive androgenetic alopecia in predisposed individuals.
- Smoking has been linked to increased alopecia risk, with stronger hair loss and premature graying among smokers.
- Diet and nutrient deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, protein) contribute to hair shedding, particularly in telogen effluvium cases.
- Stress triggers acute hair loss episodes, especially telogen effluvium.
- In alopecia areata, the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, producing patchy hair loss.
- Medical treatments and conditions like chemotherapy, thyroid disease, diabetes, and hypertension medications can all be causal.
- Chronic traction (tight hairstyles), harsh chemical treatments, and pollution may accelerate hair loss.
- A recent genomic study found specific allelic variants for androgenetic alopecia, but also a strong influence from nutritional and lifestyle variables.
- Having a “baldness gene” increases risk, but expression depends on many modifiable and non‑modifiable factors.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
- Twin and family studies suggest the heritability of male pattern baldness may reach 80%, meaning shared genetics are the major determinant.
- The gene encoding the androgen receptor (AR) is strongly linked to pattern hair loss, but many other genes are involved.
- Androgenetic alopecia affects about 50 million men and 30 million women in the U.S., many with inherited predisposition.
- In the Indian sample noted earlier, 70.5% of individuals with hair loss reported a positive family history.
- Genetic predisposition alone does not guarantee hair loss; environmental triggers and lifestyle factors modulate onset and progression.
- Some studies estimate that 60% of hair loss vulnerability arises from genetic causes.
- Female pattern hair loss often has a slower progression, less hairline recession, and occurs later in life, though still genetically driven.
- Men whose fathers were bald have a 5 to 6 times higher relative risk of balding compared to those whose fathers were not affected.
- Inheritance patterns are complex, and genetics serve as a marker of risk rather than a definitive predictor.
Hair Loss and Lifestyle Factors
- Smokers show higher rates of hair loss compared to non‑smokers.
- A 2023 study called out stress and psychosocial factors as significant contributors to increased hair shedding.
- Adults lacking adequate iron, protein, or vitamin B12 are at elevated risk of hair shedding.
- Excessive hair styling, tight hairstyles, frequent chemical treatments, and dehydration are linked with increased hair loss in younger age groups.
- Alcohol and sugary beverages are correlated with hair loss risk.
- Sleep deprivation and chronic fatigue interfere with the body’s repair cycles.
- Urban pollution, smoking, and oxidative stress are implicated in accelerating hair root aging and follicle damage.
- Lifestyle factors alone rarely cause full baldness in genetically low-risk individuals, but they can advance the onset or worsen the progression in those predisposed.
Medical Conditions and Hair Loss
- Medical conditions like thyroid disease, lupus, and diabetes are commonly associated with hair loss.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects 1 in 10 women of reproductive age in the U.S., often causing androgenic hair thinning.
- Anemia, particularly iron deficiency anemia, is a frequent and reversible cause of diffuse hair loss.
- Chemotherapy leads to anagen effluvium, a sudden and widespread loss of hair within days to weeks of treatment.
- Autoimmune diseases such as alopecia areata cause patchy hair loss by attacking hair follicles.
- Individuals with scalp psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis may experience shedding due to inflammation and scaling.
- Hormonal imbalances, such as low estrogen or high testosterone, contribute to hair thinning, especially in women.
- High blood pressure medications, including beta blockers and ACE inhibitors, have been linked to drug-induced hair shedding.
- Hair loss is also a common side effect of antidepressants, anticoagulants, and retinoids.
- A 2023 study found that 26.3% of individuals with alopecia had one or more comorbid chronic illnesses.
Hair Loss Symptoms and Signs
- Gradual thinning on top of the head is the most common symptom, often starting at the temples or crown.
- A receding hairline is typically the first noticeable sign in men with androgenetic alopecia.
- In women, widening of the part or overall diffuse thinning is more common than frontal recession.
- Patchy or circular bald spots can occur with conditions like alopecia areata, usually on the scalp but sometimes eyebrows or beard.
- Sudden loosening of hair, noticeable when combing or after showering, may indicate telogen effluvium caused by stress or illness.
- Full-body hair loss may result from certain medical treatments, such as chemotherapy or autoimmune diseases.
- Scaly patches and inflammation can accompany fungal infections like tinea capitis, leading to broken hairs and bald patches.
- Hair breakage rather than root loss often signals external damage from styling or chemical treatments.
- Increased hair shedding during brushing or washing, particularly when it persists over several weeks, may suggest early-stage hair loss.
- Itching or burning sensations on the scalp may precede or accompany some forms of alopecia or dermatitis.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
- 78% of women experiencing hair loss report feelings of shame, anxiety or depression.
- Individuals with hair loss had a 34% higher risk of developing major depressive disorder.
- Participants suffering from stress were 3.04 times more likely to experience hair loss.
- Hair loss is linked with body image dissatisfaction.
- Many report feelings of helplessness or preoccupation with further hair loss.
- Nearly 30% of women with hair loss exhibit two or more signs of depression.
- Women with hair loss often avoid social engagements.
- For many men, hair loss leads to compensatory behaviours, such as growing facial hair or getting tattoos.
Hair Loss and Self‑Esteem
- 85% of women with hair thinning report a negative effect on self-esteem.
- Affected women scored significantly lower on self-rated wellness.
- Hair loss often triggers a downward self-image spiral.
- 28% reported interference in daily functioning six months post-treatment.
- Women over 50 frequently cite career impact linked to thinning hair.
- Men aged 45‑54 are more likely to pre‑empt hair loss by shaving their heads.
- Hair loss may cause “psychological stress out of proportion to the problem.”
Economic/Market Statistics (Global and Country‑wise)
- The global hair loss market was valued at $52.37 billion in 2022 and projected to exceed $88 billion by 2030.
- American consumers will spend $2.22 billion on hair loss products in 2025.
- The hair loss treatment products market is estimated at $2.93 billion in 2025.
- In India, the market was valued at $282.41 million in 2024 and projected to reach $539.46 million by 2033.
- The hair thinning market is expected to reach $2.75 billion by 2030.
- Women accounted for 71.03% of the product revenue in 2024.
- Shampoos and conditioners held 88.21% share in 2024.
- North America held 36.05% of the market share in 2024.
Hair Loss Treatment Statistics
- The market is projected at $4.78 billion in 2025, growing to $7.28 billion by 2032.
- The U.S. holds 32% of the global share in 2023.
- Global hair regrowth treatments to reach $7.80 billion in 2025.
- Minoxidil is projected to hold 47.8% of the global regrowth market share in 2025.
- Men’s segment expected to account for 63.4% of treatment revenue in 2025.
- 66.4% of respondents used finasteride 1 mg.
- 56.8% used 5% minoxidil foam.
- 10.2% reported use of oral minoxidil.
- The market is shifting toward pharmaceutical solutions.
Most Used Hair Loss Treatments
- Topical minoxidil remains a frontline option.
- Oral finasteride continues to be widely prescribed.
- Shampoos and conditioners dominate product type share.
- Supplement and laser device categories are growing.
- Combination therapies are gaining traction.
- Female treatments often include hormonal evaluation.
- Many users turn to prevention strategies earlier.
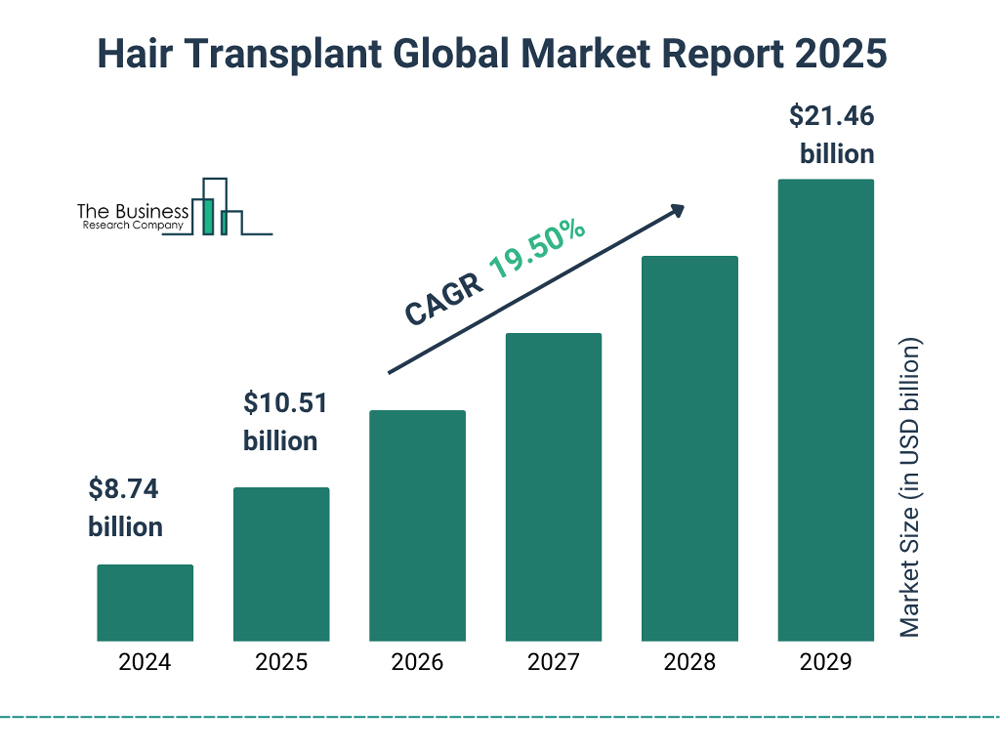
Hair Transplant Statistics
- The global hair transplant market is projected to grow rapidly, reaching $10.51 billion by 2025.
- Market size in 2024 is estimated at $8.74 billion, showcasing significant year-over-year growth.
- Expected CAGR: 19.50% — highlighting strong industry momentum and rising demand.
- Continued expansion anticipated, with revenues forecasted to climb to $21.46 billion by 2029.
- Annual market progression:
- 2024: $8.74 billion
- 2025: $10.51 billion
- 2026: continued growth (visual trend indicates strong upward trajectory)
- 2027–2028: steady expansion aligned with CAGR estimate
- 2029: projected peak at $21.46 billion
- Growth driven by increasing adoption of hair restoration procedures and rising awareness of advanced transplant technologies.
- Data sourced from The Business Research Company, reflecting credible market analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Around 85% of men will experience hair loss during their lifetime.
The global alopecia market is forecast to reach approximately $$11.6 billion in 2025.
In a dataset of 1,009,998 users, 86.4% reported visible hair loss (43.7% mild, 31.6% moderate, 11.2% severe).
The global hair loss treatment market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2025 to 2032.
About 23% of women aged 18‑65 say their hair has gotten thinner, compared with 18% of men.
Conclusion
Hair loss is not just a cosmetic concern; it touches emotional well-being, self-esteem, and major global markets. From the 78% of women reporting anxiety tied to thinning hair to the multi-billion dollar growth in hair loss treatments and transplants, the data show a clear and multi-dimensional trend. For U.S. audiences and beyond, understanding these statistics helps clarify both the scale of the challenge and the opportunities for solutions. Dive into this full article to explore the deeper insights.


