Remote work has shifted from a pandemic-era experiment to a mainstay of modern business. As employees log in from home offices, cafes, and co-working spaces, the cybersecurity landscape has expanded with them. Organizations now face a broader attack surface, driving demand for stronger defenses and smarter policies. From healthcare to tech firms, businesses of all sizes are grappling with remote work-linked breaches and rising attack sophistication, a trend with real consequences for operations and reputation. Explore the stats below to understand how remote work impacts cybersecurity.
Editor’s Choice
- 42% of workers log in remotely at least once a week in 2025, increasing exposure to cyber risk.
- 78% of organizations reported at least one security incident linked to remote work in 2025.
- $4.44M is the global average cost of a data breach in 2025.
- 60% of companies cite phishing as the top remote work threat vector.
- 73% of remote employees use personal devices for work, often without strong security.
- 91% of cybersecurity professionals say attacks increased due to remote work.
- 90% of IT professionals express confidence in their remote security measures, despite existing gaps.
Recent Developments
- 72% of organizations report a year-over-year rise in perceived cyber risk.
- High-profile breaches in 2025 continue to expose weaknesses in remote access configurations.
- Remote job scams have emerged as a new threat, with attackers impersonating legitimate employees or contractors.
- Automated AI-driven scans reached 36,000 per second globally, targeting exposed remote services.
- Credential theft increased by 160% in 2025, driving unauthorized access incidents.
- Malicious URLs and advanced social engineering are now more common than file-based malware.
- Ransomware and business email compromise continue to exploit remote work patterns.
- Zero Trust adoption is accelerating as organizations move away from perimeter-based security.
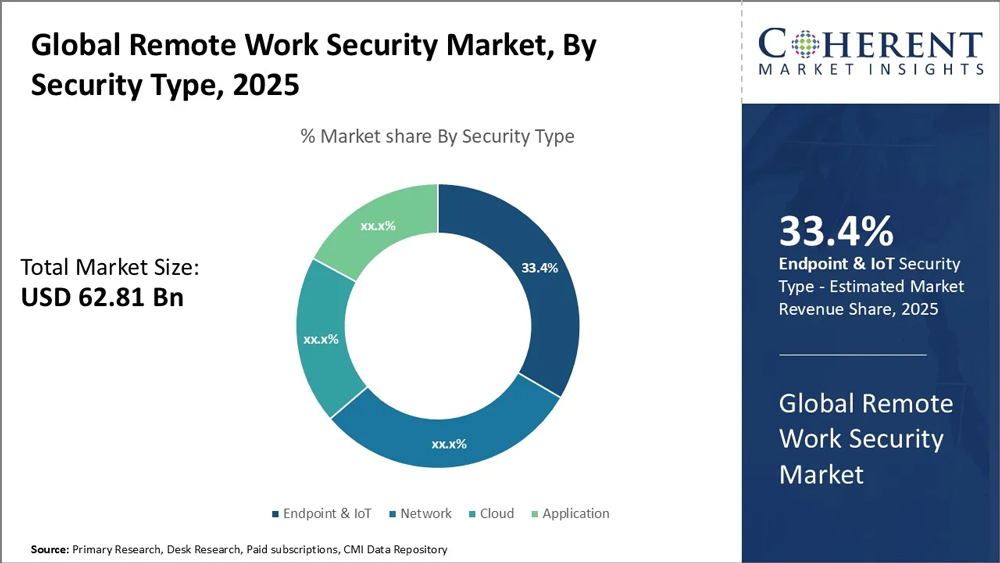
Global Remote Work Security Market Breakdown
- The global remote work security market is valued at USD 62.81 billion in 2025, reflecting strong enterprise spending on securing distributed workforces.
- Endpoint & IoT Security leads the market with a 33.4% share, making it the largest security segment in remote work environments.
- The dominance of endpoint-focused solutions highlights the rapid increase in remote devices, laptops, and IoT endpoints used by employees.
- Network Security accounts for a significant but unspecified percentage, emphasizing the continued need to secure VPNs, remote access, and corporate networks.
- Cloud Security represents a notable portion of the market, driven by rising reliance on cloud platforms and SaaS tools for remote collaboration.
- Application Security contributes a meaningful share, reflecting growing concerns around web apps, internal tools, and remote access applications.
- The market structure indicates a multi-layered cybersecurity approach, where organizations invest across endpoint, network, cloud, and application security to reduce remote work risks.
Remote Work Cybersecurity Statistics Overview
- 78% of companies experienced at least one remote work-related security incident in 2025.
- 91% of cybersecurity professionals observed an increase in attacks tied to remote work practices.
- Global cybercrime costs are projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Phishing remains the most common initial access vector for remote breaches.
- Breaches involving remote work factors carry higher average costs than office-based incidents.
- Only 3% of organizations demonstrate mature cyber resilience.
- Cybersecurity talent shortages continue to raise breach impact and recovery costs.
- Average breach detection and containment time remains lengthy at roughly 241 days.
Global Remote Work Adoption and Scale
- 42% of the global workforce logs in remotely at least weekly in 2025.
- In the U.S., 27% of employees are fully remote and 52% work in hybrid roles.
- Hybrid work continues to expand as organizations adopt flexible workforce models.
- 83% of employees worldwide prefer hybrid work arrangements.
- The remote work security market is growing steadily due to rising demand.
- Small businesses show high remote adoption but often lag in cybersecurity maturity.
- Organizations with strong security frameworks are more likely to support remote work.
- Remote work expands the security perimeter beyond traditional office networks.
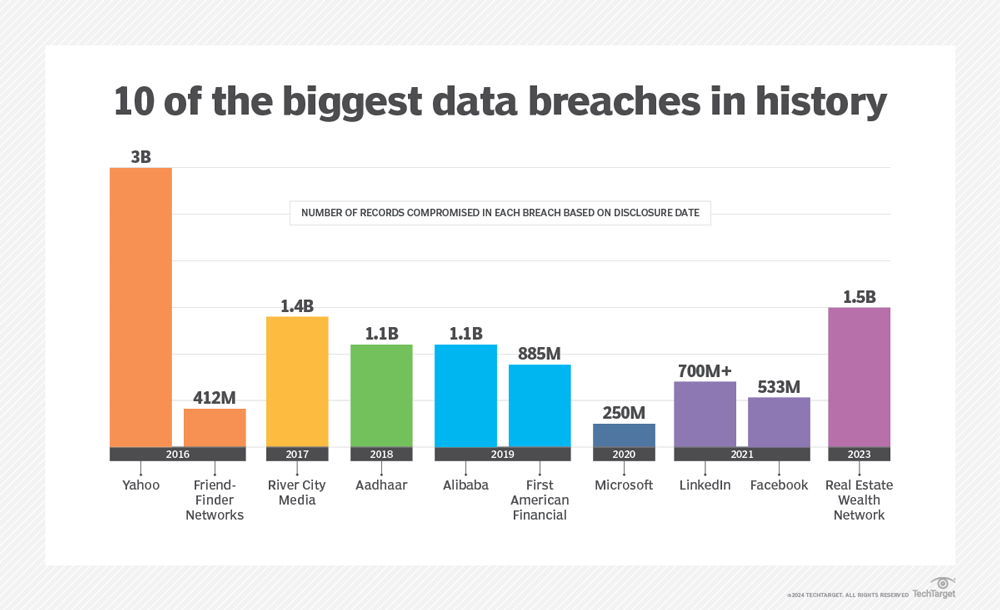
Biggest Data Breaches in History
- Yahoo holds the record for the largest data breach ever, with 3 billion user accounts compromised in 2016, impacting nearly its entire user base.
- Real Estate Wealth Network suffered a massive 2023 breach, exposing 1.5 billion records, making it one of the largest recent data leaks on record.
- In 2017, River City Media experienced a breach affecting 1.4 billion records, highlighting risks in email marketing databases.
- India’s national ID system, Aadhaar, was linked to a breach in 2018, exposing 1.1 billion records, raising serious privacy and national security concerns.
- Alibaba reported a breach in 2019 that compromised 1.1 billion user records, underscoring vulnerabilities in large-scale e-commerce platforms.
- First American Financial disclosed a 2019 incident involving 885 million records, one of the largest financial-sector data exposures.
- LinkedIn saw data from 700 million+ users scraped and exposed in 2021, emphasizing ongoing risks to professional networking platforms.
- Facebook also faced a major 2021 breach, with 533 million user records leaked, affecting users across multiple countries.
- Friend Finder Networks reported a 2016 breach exposing 412 million accounts, one of the largest incidents involving adult social platforms.
- Microsoft disclosed a 2020 data exposure involving 250 million customer support records, highlighting risks even for top-tier technology firms.
Remote Work Cybersecurity Incident Rates
- 78% of organizations report cybersecurity incidents linked to remote work in recent surveys.
- 63% of businesses faced data breaches triggered by remote work environments.
- 80% surge in email phishing attacks targets remote workers effectively.
- 30% increase in unauthorized access incidents due to remote work vulnerabilities.
- 58% of companies with remote work report rising insider threats.
- 60% of remote workers use unsecured personal devices, heightening breach risks.
- 67% of medium businesses and 74% of large ones suffer cyber breaches annually.
- 42% of organizations faced phishing and social engineering attacks in 2024.
- 82% of companies note increased cyber threats post-remote work transition.
Data Breach Costs Linked to Remote Work
- $4.44M represents the global average cost of a data breach in 2025.
- The average breach cost in the U.S. reached $10.22M.
- Remote work as a factor in a data breach increases the average cost by about $131,000, with the global average breach cost at $4.44 million in 2025.
- Skills shortages correlate with 43% higher breach expenses.
- Breaches involving remote access technologies take longer to contain.
- Healthcare and financial services record the highest per-incident costs.
- Phishing-driven breaches often generate greater financial damage.
- Remote work expands third-party and cloud-related breach exposure.
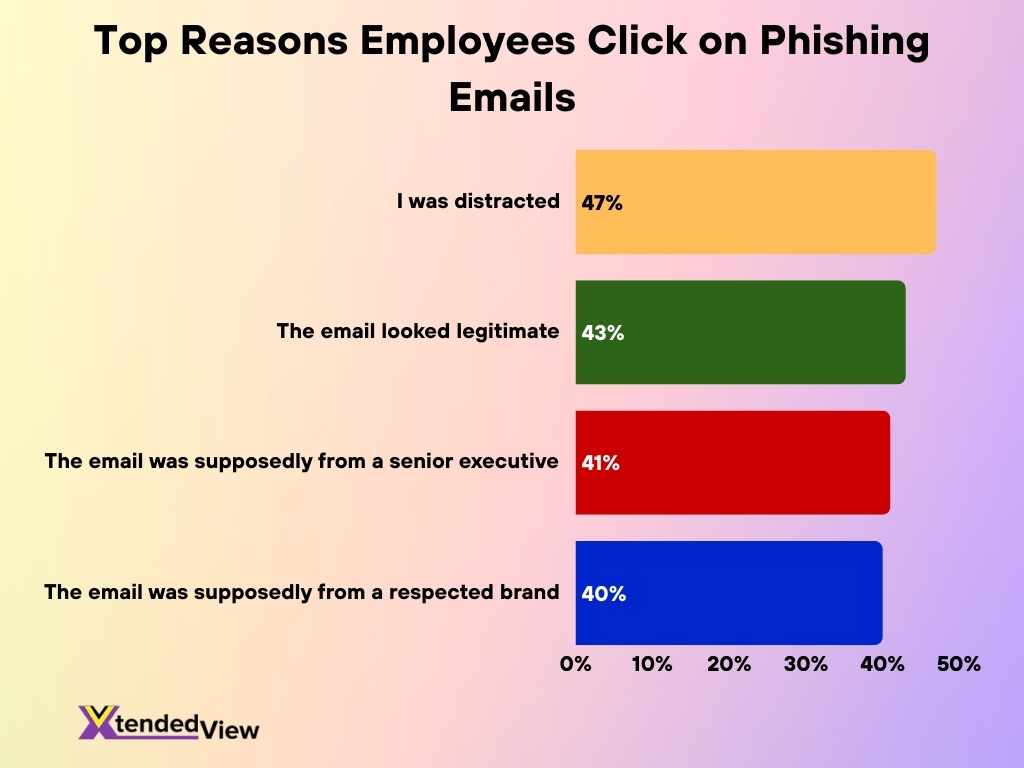
Why Employees Fall for Phishing Emails
- 47% of employees admit they clicked on a phishing email because they were distracted, highlighting how inattention during busy work hours increases cyber risk.
- 43% of employees were fooled because the email appeared legitimate, showing how well-crafted phishing messages can bypass visual trust checks.
- 41% of employees clicked after believing the email was from a senior executive, underscoring the effectiveness of authority-based phishing attacks.
- 40% of employees trusted phishing emails that claimed to come from a respected brand, proving that brand impersonation remains a powerful social engineering tactic.
Common Remote Work Cyber Threats
- Phishing drives over 80% of reported security incidents affecting remote workers.
- Phishing accounted for roughly 16% of all data breaches in 2025.
- 57% of organizations experience phishing attempts weekly or daily.
- Ransomware appeared in about 44% of breach incidents.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks increase on unsecured remote networks.
- Smishing and voice-based phishing surged sharply in 2025.
- AI-driven social engineering raises attack success rates.
- Unpatched personal devices and home networks widen attack surfaces.
- Remote monitoring tools are increasingly abused to deploy malware.
Ransomware Targeting Remote Environments
- Ransomware attacks occur every 19 seconds globally in 2025, totaling over 11,000 daily attempts.
- Ransomware featured in approximately 44% of data breaches reported in 2025.
- Double-extortion tactics dominate with 70% of attacks combining data theft and encryption.
- Exposed RDP services account for a significant portion of ransomware entry points, often via weak security.
- 37% of ransomware victims are companies with fewer than 100 employees, lacking remote containment tools.
- Ransomware remediation averages 24 days of downtime, longer than typical breaches at 23-27 days.
- BYOD policies in remote setups heighten risks, with 42% working remotely weekly, and unmanaged devices are vulnerable.
- Small teams face 81% of successful attacks targeting under 1,000-employee firms needing extended forensics.
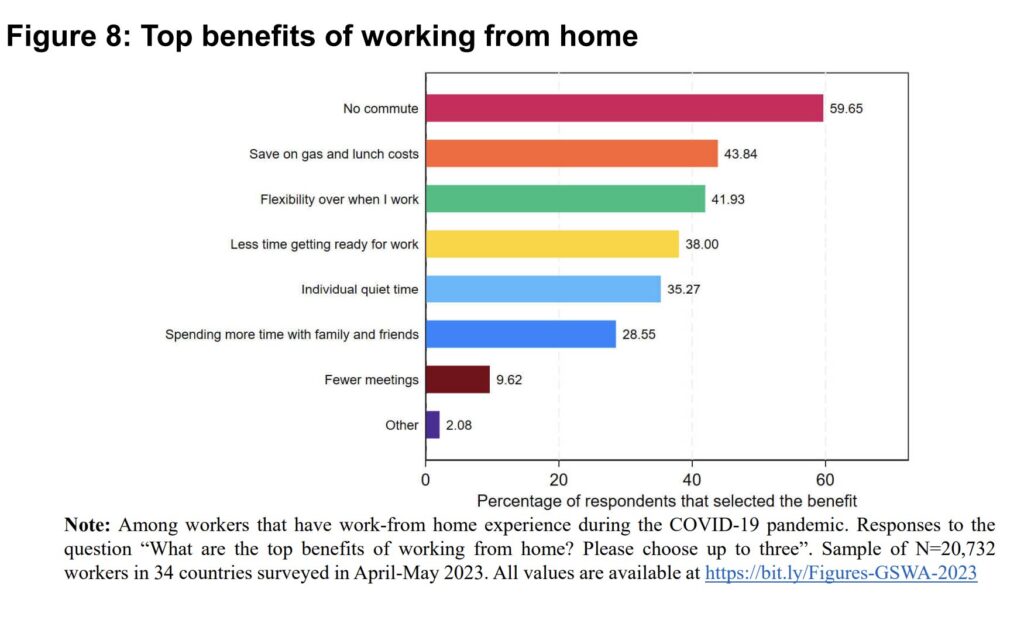
Top Benefits of Working From Home
- No commute stands out as the biggest advantage, with 59.65% of respondents citing it as their top benefit, highlighting major time savings and reduced daily stress.
- Saving on gas and lunch costs is a strong financial motivator, selected by 43.84% of workers, showing how remote work directly reduces everyday expenses.
- Flexibility over when employees work ranks high, with 41.93% valuing the ability to control their schedules and productivity hours.
- Less time spent getting ready for work benefits 38.00% of respondents, emphasizing improved daily efficiency and convenience.
- Individual quiet time is important for 35.27%, reinforcing how work-from-home setups support better focus and fewer distractions.
- Spending more time with family and friends matters to 28.55%, underlining the positive impact of remote work on work–life balance.
- Fewer meetings is a comparatively smaller benefit, mentioned by only 9.62%, suggesting remote work does not significantly reduce meeting frequency.
- Other benefits were selected by just 2.08%, indicating that the primary advantages of remote work are well-defined and widely shared across respondents.
Credential Theft and Account Compromise Statistics
- Credential theft surged by 160% in 2025 compared to 2024.
- Stolen credentials drove 22% of all breaches in 2025.
- Infostealer malware stole 1.8 billion credentials from 5.8 million devices in 2025.
- 56% of Q1 2025 compromises used stolen credentials without MFA.
- Credential stuffing made up 19% of daily authentication attempts in 2025.
- 80% of lateral movement exploits compromised credentials.
- Cloud credential breaches take 292 days to detect on average.
- 39% of cloud businesses faced admin account compromise in 2023-2025.
- Credential-based breaches cost $4.8 million on average with 186-day identification.
Remote Access, VPN, and RDP Security Statistics
- Over 90% of analyzed cyber attacks in 2023 abused RDP services, marking the highest rate since 2020.
- 92% of organizations worry that VPN vulnerabilities directly enable ransomware attacks.
- VPNs and firewalls account for 58% of all ransomware incidents.
- Remote access tools served as the initial entry in 80% of ransomware attacks in 2024.
- RDP exploitation occurred in 90% of cases analyzed last year by Sophos.
- 48% of organizations faced VPN-related cyberattacks, 30% with multiple incidents.
- 87% of Zero Trust adopters report a significant decrease in security incidents.
- MFA adoption for workforce users reached 66% as of January 2024.
- 65% of organizations plan to replace VPNs with Zero Trust solutions this year.
- 50% of Q3 2025 ransomware attacks began with remote access abuse.
Cloud and SaaS Security Risks in Remote Work
- Cloud incidents contribute to 21% of reported breaches.
- 27% of organizations report cloud security challenges tied to misconfigurations.
- 88% of cloud breaches stem from human error.
- Remote workers often access SaaS tools without identity controls.
- Identity remains the weakest link in SaaS security.
- Data loss prevention adoption continues to rise.
- API vulnerabilities and exposed endpoints enable data exfiltration.
- Remote work accelerates cloud usage without centralized governance.
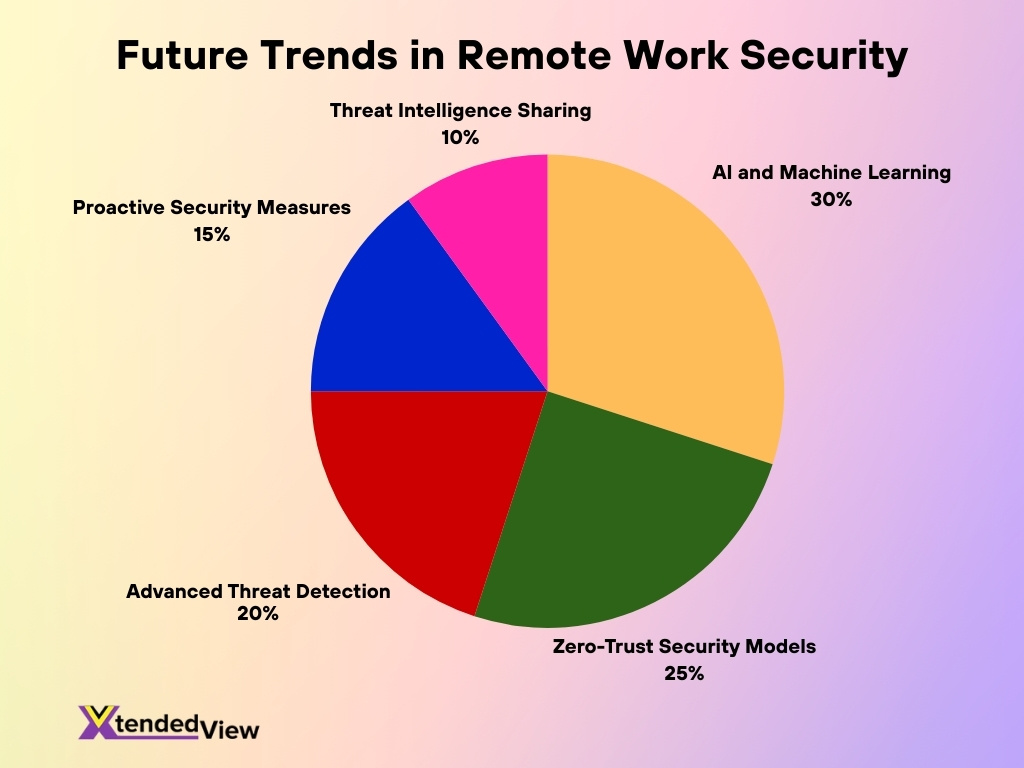
Future Trends Shaping Remote Work Security
- Threat Intelligence Sharing stands at 10%, indicating a steady but smaller focus on collaborative cybersecurity intelligence and information exchange.
- AI and Machine Learning lead future investments, accounting for 30%, as organizations rely on automation, behavioral analytics, and predictive threat prevention.
- Zero-Trust Security Models represent 25%, reinforcing the shift toward continuous identity verification and least-privilege access for remote employees.
- Advanced Threat Detection captures 20%, highlighting the growing need for real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and rapid incident response.
- Proactive Security Measures make up 15%, reflecting increased emphasis on preventive controls, risk assessment, and early threat mitigation.
Shadow IT and Unmanaged Device Exposure
- 85% of businesses experienced cyber incidents, with 11% tied to shadow IT.
- 60% of organizations fail to include shadow IT in risk assessments.
- 55% of employees adopt unauthorized SaaS tools.
- Shadow IT inflates IT spending by 30% to 40% in large enterprises.
- Unsanctioned tools often lack encryption and monitoring.
- 72% of generative AI use occurs outside IT oversight.
- Small businesses report high shadow AI adoption on unmanaged devices.
- Shadow IT breaches cost more due to limited visibility.
Personal Device and BYOD Usage Statistics
- 44% of employees use personal phones for work tasks.
- 32% of workers use personal computers for work activities.
- Even where BYOD is banned, 78% still use personal devices.
- 40% of edge devices remain unmanaged.
- 38% of IT teams lack visibility into connected devices.
- Unmanaged devices link to over 90% of ransomware incidents.
- Credential reuse and weak configurations heighten BYOD risk.
- Weak BYOD policies correlate with higher data leaks.
Home Network and Wi-Fi Security Weaknesses
- 86% of users never change their router admin passwords, leaving networks exposed to attacks.
- 79% of home Wi-Fi networks use weak passwords vulnerable to cyber attacks.
- 89% of households never update router firmware, retaining exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Nearly 50% of household IoT devices contain critical vulnerabilities.
- 57% of IoT devices are vulnerable to medium- or high-severity attacks.
- The average smart home faces over 12,000 hacker attacks per week.
- 25% of public Wi-Fi users in cafes report identity compromise incidents.
- 98% of IoT device traffic travels unencrypted, enabling interception.
- Routers comprise over 50% of the most critically vulnerable devices in networks.
- 72% never change Wi-Fi passwords from factory defaults.
Remote Work Cyber Risks by Industry
- Healthcare experienced 1,710 security incidents with 1,542 data disclosures in remote setups.
- Finance and healthcare breaches cost $1.07 million more when remote work factors in.
- 18% of SMBs report inadequate security controls amid remote vulnerabilities.
- Retail saw phishing cause 25% of threats, with frequent credential theft.
- Technology firms faced 57% API-related breaches in the past two years.
- Manufacturing reported 41% attack increasein attacks targeting remote supply chains.
- Education saw 34% rise in phishing among remote faculty and students.
- Professional services identified 49% data leakage from weak remote policies.

Employee Cybersecurity Awareness and Training Gaps
- 40% of employees receive no cybersecurity training.
- Continuous training can reduce phishing success by 50%.
- 43% of security leaders cite employee distraction as a top risk.
- Human error contributes to 90% of successful attacks.
- Only 46% of workers correctly identify AI-generated phishing.
- Untrained employees are three times more likely to mishandle data.
- Personal device safety awareness remains low.
- Ongoing education directly impacts breach susceptibility.
Zero Trust and Remote Access Security Adoption
- Only 81% of organizations have adopted or are implementing Zero Trust models.
- 72% of global enterprises actively pursue Zero Trust frameworks per the Gartner 2025 Index.
- 79% of organizations allow remote access from personal devices, heightening security needs.
- 54% of CISOs report increased credential theft from remote access tools in 2025.
- 87% of Zero Trust adopters see significant drops in security incidents.
- Organizations with Zero Trust report 50% faster incident response times.
- Zero Trust cuts insider threats by 68% through continuous verification.
- 78% of breaches are preventable with full Zero Trust adoption, including micro-segmentation.
- 58% of enterprises use micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement in Zero Trust.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Password Hygiene Stats
- 83% of SMBs require MFA for all employee resources.
- 87% of enterprises with over 10,000 employees use MFA, compared to 34% of SMBs.
- 44% of companies mandate MFA for remote access.
- 94% of passwords are reused across multiple accounts.
- 81% of hacking-related breaches stem from weak or stolen passwords.
- MFA blocks 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
- The passwordless authentication market is expected to hit $22 billion in 2025.
- Phishing-resistant MFA stops 30-50% of advanced attacks.
- 54.8% of Google Cloud breaches were from weak passwords.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
92% of IT professionals say that remote work has increased cybersecurity threats in 2025.
42% of workers log in remotely at least once a week in 2025.
42% of organizations reported a successful social engineering attack, or phishing, against remote workers in the past year.
Ransomware attacks and social engineering risks increased by 53% in remote/hybrid work environments.
Remote work as a factor in a breach increases the cost by about $131,000 on average.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity for remote work is a critical battleground where organizations must balance flexibility with protection. Home networks, personal devices, and human behavior expand attack surfaces. While MFA and Zero Trust adoption strengthen defenses, gaps in training and unmanaged endpoints continue to expose risk. As remote work expands, identity-focused security, cloud controls, and continuous education will define resilience for distributed workforces.


