AI Replacing Jobs Statistics 2025
Artificial intelligence is no longer just a tool of science fiction; it’s reshaping the labor market. As AI systems grow more capable, entire job categories are being rethought across sectors like manufacturing, finance, and customer service. In banking, for instance, AI-driven tools are automating regulatory reporting and accelerating loan underwriting. In healthcare, AI is assisting radiologists with diagnostic imaging, freeing them to focus on patient care. This article unpacks the latest statistics around AI replacing jobs and explores its broad implications.
Editor’s Choice
- In 2025, AI-linked productivity growth is estimated to rise fourfold in firms that adopt it aggressively.
- Jobs requiring AI or automation skills now offer a 56 % wage premium over comparable non-AI roles.
- Roughly 27 % of AI‑using firms report that they’ve used AI to replace tasks performed by workers.
- Big Tech firms cut new graduate hiring by 25 % in 2024 compared to 2023, partly due to AI replacing entry-level roles.
- LinkedIn reported that AI‑related job postings grew 38 % from 2020 to 2024.
- The World Economic Forum’s 2025 report states 40 % of employers expect to reduce the workforce where tasks can be automated.
- Goldman Sachs projects that AI adoption may raise U.S. unemployment by 0.5 percentage points during the transition.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, the automation scores, measuring task exposure, averaged 0.29, slightly lower than 0.30 in 2023.
- McKinsey data shows 34 % of employees expect to use generative AI on more than 30 % of their daily tasks within a year.
- In April 2024, there were 14,117 AI‑related job vacancies, up 32 % year over year.
- In 2025, 1.8 % of U.S. job postings demand AI skills, up from 1.4 % in 2023.
- Indeed’s 2024 Future of Work survey finds 7 in 10 U.S. workers believe AI will “match” them to better jobs rather than simply replace them.
- Entry-level roles may see the earliest disruption, with some predicting that 50 % of entry-level white‑collar jobs could be affected in 1–5 years.
- Generative AI is expanding automation risk, especially in media, design, and web-related occupations.
- AI adoption increases demand for higher cognitive and social skills in roles that integrate generative AI tools.
Key Statistics on AI Replacing Jobs
- Up to 300 million full‑time jobs globally could be exposed to generative AI automation.
- In the U.S., AI adoption correlates with declines in employment-to-population ratios from 2010 to 2021.
- 41 % of employers globally plan to reduce their workforce in the next five years due to AI automation.
- The Future of Jobs report anticipates 9 million jobs lost globally by 2025 due to AI, with 11 million new.
- Jobs in high-AI exposure sectors see up to 4.8× greater labor productivity growth.
- About 60 % of jobs in advanced economies might be impacted, positively or negatively, by AI.
- In the U.S., software developer jobs will grow 17.9 % between 2023 and 2033, partially driven by AI demand.
- Approximately 27 % of AI‑using firms say they deployed AI to replace tasks.
- AI roles frequently command a 56% wage premium versus non‑AI roles.
AI’s Current Impact on the Job Market
- Around 16 % of U.S. workers report that at least some of their work is already done with AI.
- 52 % of workers say they’re worried about AI reducing their job opportunities, 32 % believe it already will.
- Among AI users, 73 % are under age 50, while among non‑users, 65 % are under 50.
- AI adoption is disproportionately felt by lower‑ and middle‑income workers, who more often believe AI will reduce job opportunities.
- Over three years, the share of AI‑doable tasks in job ads fell by 19 %, largely from hiring fewer AI‑eligible roles.
- Big Tech firms slashed graduate hiring by 25 % in 2024 versus 2023.
- In 2025, 1.8 % of U.S. job listings require AI skills, up from 1.4 % in 2023.
- Roles integrating generative AI list 36.7 % higher cognitive demands and 5.2 % more social skills.
- Workers in AI-demanding roles often receive more non‑wage benefits, such as remote work, than equivalent non-AI roles.
AI’s Potential Impact on the Job Market
- U.S. unemployment may rise by 0.5 percentage points during the AI transition.
- With full AI integration, labor productivity may rise about 15 % in developed markets.
- The World Economic Forum expects 11 million new jobs will emerge by 2025, even as 9 million jobs disappear.
- Jobs deeply exposed to AI see 4.8× higher productivity growth relative to low-exposure roles.
- Within one year, 34 % of employees expect to use generative AI for over 30 % of tasks.
- 60 % of jobs could feel some effect, positive or negative, from AI’s growth.
- By 2033, software developers will grow 17.9 %, database admins 8.2 %, and architects 10.8 %, driven partly by AI tools.
- Automation scores are shifting, with a 2025 mean score of 0.29 vs 0.30 in 2023, showing variability tightening.
- Complementary skills like creativity and digital literacy will gain demand more than substitution skills will shrink.
Job Displacement Versus Job Transformation
- AI’s complementary effect is about 50 % larger than its substitution effect.
- Only 27 % of firms report using AI to outright replace tasks.
- Up to 50 % of occupations could experience high exposure to displacement in the next decade.
- Skills for AI‑exposed jobs are changing 66 % faster than for other jobs.
- Administrative sectors may lose 1 million jobs by 2029 due to automation.
- Roles are being redefined, with AI handling repetitive subtasks while humans oversee and engage clients.
- In mature AI sectors, firms report no net layoffs because transformed roles absorb displaced workers.
- Displaced workers often bear short‑term costs, while firms and economies benefit later.
Jobs Most Likely to Be Replaced by AI
- AI could automate 50 % + of tasks in market research and sales representative roles.
- Entry‑level roles in customer service, data entry, and telemarketing are at the highest risk.
- Roles such as interpreters, translators, attendants, and sales reps are among the top 40 most AI‑vulnerable.
- 40 % of programming tasks could be automated by 2040, threatening entry-level coding jobs.
- AI may replace 300 million full‑time jobs globally, about 9 % of all jobs.
- Manufacturing could lose as many as 2 million jobs by 2025.
- Structured white‑collar roles are more exposed than creative or ambiguous ones.
- AI has already contributed to a 13 % decline in early‑career employment in exposed roles.
Jobs Least Likely to Be Replaced by AI
- Healthcare and education roles remain safer due to human judgment and empathy.
- Creative jobs fare better where novelty and emotional expression matter.
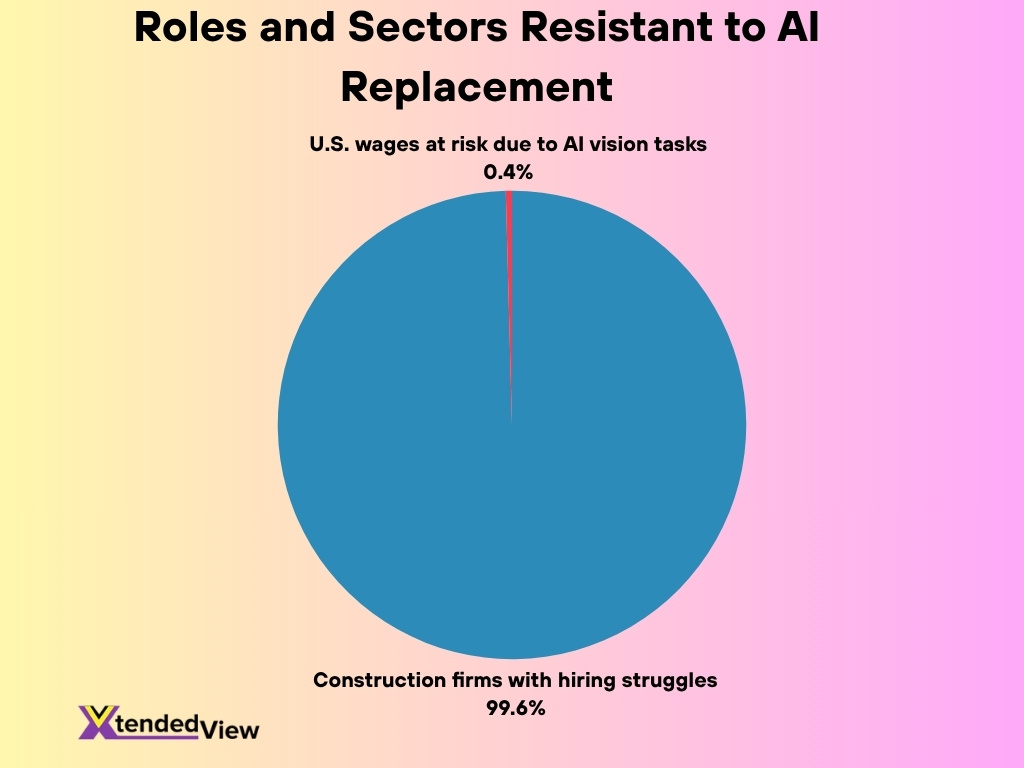
- Skilled trades show lower automation risk, with 94 % of construction firms struggling to fill roles.
- Only 0.4 % of U.S. wages may be at risk due to AI vision‑based tasks.
- Jobs requiring unpredictability and emotional intelligence resist automation more strongly.
- Low-risk occupations may still change, but overall job loss risk remains low.
- Caregiving roles remain difficult for AI to replicate authentically.
- Design and visual tasks are among the hardest for AI to replace.
AI Replacing Work Tasks
- By 2030, 30 % of U.S. jobs could be fully automated, while 60 % will see significant task change.
- AI handles subtasks like data parsing and basic drafting rather than full roles.
- Generative AI could automate 30 % of hours worked in the U.S. by 2030.
- Routine cognitive tasks are displaced faster than nonroutine or social ones.
- Administrative tasks like scheduling and email drafting are being automated.
- Some tasks within roles shrink while oversight tasks remain human.
- Law and accounting see AI in contract review and audit sampling.
- Vision-based tasks remain hard to automate.
Notable Jobs and Tasks AI Can’t Replace
- AI cannot replicate emotional intelligence, ethical judgment, or genuine empathy.
- Strategic vision and innovation remain human domains.
- Negotiation, crisis management, and high-stakes decision making resist automation.
- Leadership roles involving culture and people management remain human.
- Human oversight and accountability tasks cannot be automated by AI itself.
- Creative direction and metaphorical thinking are uniquely human.
- Roles combining physical presence and adaptation resist AI substitution.
- Adaptive problem-solving in novel contexts remains a gap for AI.
Impact of AI Across Different Industries
- Manufacturing has eliminated over 1.7 million jobs globally due to automation.
- High‑AI exposure sectors see 4.8× greater productivity growth than low-exposure ones.
- Software developer jobs will grow 17.9 % by 2033, fueled by AI.
- Retail and logistics see AI automating warehousing and inventory tasks.
- Financial services use AI for risk modeling and compliance, cutting mid-level jobs.
- In media, AI automates drafting, imagery, and summaries.
- Healthcare uses AI for diagnostics and imaging, augmenting human roles.
- Legal fields use AI for contract generation and compliance.
Global and Regional Variations in AI’s Impact
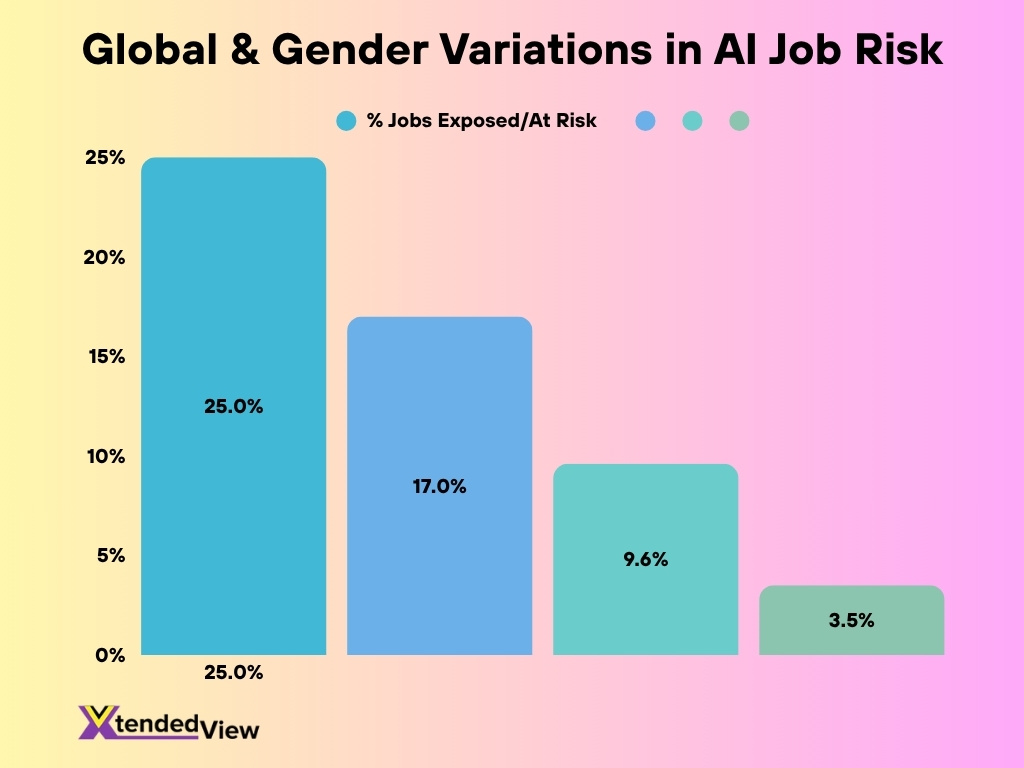
- In high-income countries, 25 % of jobs are potentially exposed to AI, compared to 17 % in lower-income nations.
- In rich regions, jobs at the highest risk make up 9.6 % of female employment versus 3.5 % of male.
- Asia-Pacific shows fast AI growth but unequal access to retraining.
- U.S. disruptions concentrate in tech hubs, with rural areas slower to adapt.
- EU and China’s industrial AI growth may buffer direct losses.
- Latin America and Africa face low automation but high vulnerability.
- In U.S. non‑IT services, women are more affected by digital tech than men.
- Regions with early AI investment show stronger job gains.
Gender and Generation Differences in AI Job Impact
- Women’s jobs are three times more likely to face replacement than men’s.
- 9.6 % of female jobs in high-income regions face high automation risk versus 3.5 % for men.
- Only 30 % of the AI workforce is female.
- Women adopt AI tools 25 % less than men.
- AI users in 2025 earn 40 % more, but women report smaller boosts.
- Younger workers saw a 6 % drop in employment in exposed roles from 2022–2025.
- Gen Z and Millennials adopt AI faster than older generations.
- The gender gap is narrowing, with 29.4 % of AI engineers now women.
Impact of AI on Wages and Skills
- AI or automation skills bring a 56 % wage premium.
- AI professionals earn 9–13 % more than data scientists.
- Median pay for AI roles in 2025 is $156,998.
- AI-exposed workers earn $33.3/hr on average, versus $20/hr otherwise.
- AI job skills evolve 66 % faster than in other fields.
- Low-skilled jobs face downward wage pressure, while high-skilled jobs rise.
- AI adoption may raise unemployment by 0.5 % during the adjustment.
Education and Skills for Future‑Proof Careers
- 69 million new jobs may be created by 2028 in AI and tech.
- AI-exposed job demand rose between 2019–2024.
- By 2025, 50 % of employees will need reskilling.
- One third of service and 14 % of manufacturing firms retrain existing staff.
- 92 % of firms plan to increase AI investment within 3 years.
- Only 1 % of organizations are fully AI-mature.
- Programs like IBM SkillsBuild expand global AI training.
- Augmentation AI raises wages while automation AI suppresses them.
How Companies and Workers Are Adapting to AI
- 33 % of service firms and 14 % of manufacturers retrain staff.
- 46 % of employees at AI-transformed firms feel job anxiety, versus 34 % elsewhere.
- Only 5 % of global firms see measurable ROI from AI investments.
- Most firms use AI to augment productivity rather than replace jobs.
- Many adopt human–AI hybrid roles and copilots.
- Only 24 % of companies link reskilling to strategy.
- Displaced workers often shift to oversight roles in AI systems.
AI’s Potential to Create New Careers
- 92 million jobs displaced by 2030, but 170 million created, a net gain of 78 million.
- Emerging titles include prompt engineer, AI ethics officer, and model auditor.
- India may see 4 million new AI jobs by 2030.
- U.S. AI jobs grew 25.2 % from 2024 to 2025.
- Cross-disciplinary AI roles are rising in law, healthcare, and design.
- Most new jobs will involve AI deployment, governance, and integration.
- Adaptability and meta‑skills will be vital as AI spawns new work categories.
AI Productivity Growth (2018–2024)
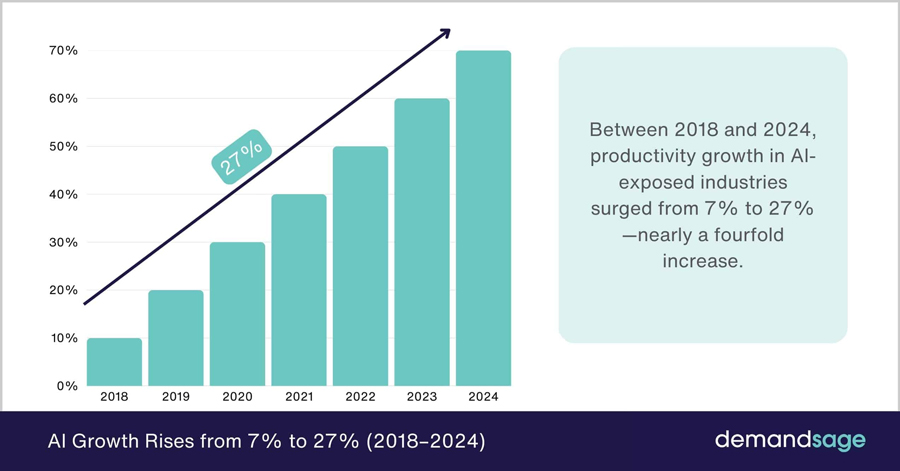
- AI-exposed industries experienced a remarkable surge in productivity growth between 2018 and 2024.
- Productivity increased from 7% in 2018 to 27% in 2024, marking a nearly fourfold rise over six years.
- The growth trend remained consistent and upward, showing steady year-over-year improvements.
- The most significant gains occurred between 2020 and 2023, where productivity jumped from 30% to 65%.
- This surge reflects the widespread adoption of AI technologies and their integration into core business processes.
- AI-driven innovation, automation, and data analytics have contributed heavily to this productivity boost.
- The data underscores that AI is becoming a major driver of efficiency, competitiveness, and long-term economic growth.
- Overall, the period 2018–2024 represents a transformative era for industries leveraging artificial intelligence.
Preparing for the Future of AI and Work
- Workers should prioritize lifelong learning, adaptability, and human-centric skills.
- Building meta‑skills like systems thinking and digital literacy helps adaptation.
- Firms and governments must invest in reskilling infrastructure.
- Policies such as portable training funds and wage subsidies can ease transition.
- Monitoring bias in AI systems is essential for fairness.
- Encouraging hybrid AI–human roles builds workforce resilience.
- Scenario planning helps anticipate multiple job futures.
- Collaboration across sectors is key to managing transition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Around 30 % of U.S. jobs could be fully automated by 2030.
Up to 300 million jobs globally could be displaced.
Workers with AI skills command a 56 % wage premium over non‑AI roles.
Software developer jobs in the U.S. are projected to grow by 17.9 % between 2023 and 2033.
83 % to 90 % of workers with a bachelor’s degree or higher are in jobs that could be highly exposed to AI transformation.
Conclusion
AI’s advance in 2025 is reshaping how work evolves, with clear evidence of job displacement, task transformation, and new job creation occurring side by side. Across industries and regions, impacts vary dramatically, and disadvantaged groups such as women and younger workers face disproportionate disruption. Yet opportunities abound, as workers with AI‑adjacent skills earn higher wages and firms find more value in augmentation than replacement. The future of work will reward those who adapt, reskill, and stay alert to new job categories.